call us
Non-surgical testicular varicocele treatment
What is varicocele embolization?
Varicocele embolization is a type of medical procedure. It redirects blood from an enlarged vein to the scrotum. Such a vein is called a varicocele. May cause pain, infertility and swelling. The radiologist uses a coil or special device to block (or embolize) the vein. This can help improve the symptoms.
The scrotum is a sac that contains the testicles, blood vessels and part of the sperm. Sperm is usually made in the testicles. They travel through the spermatic cord duct system. From there, the sperm ejaculates through the urethra.
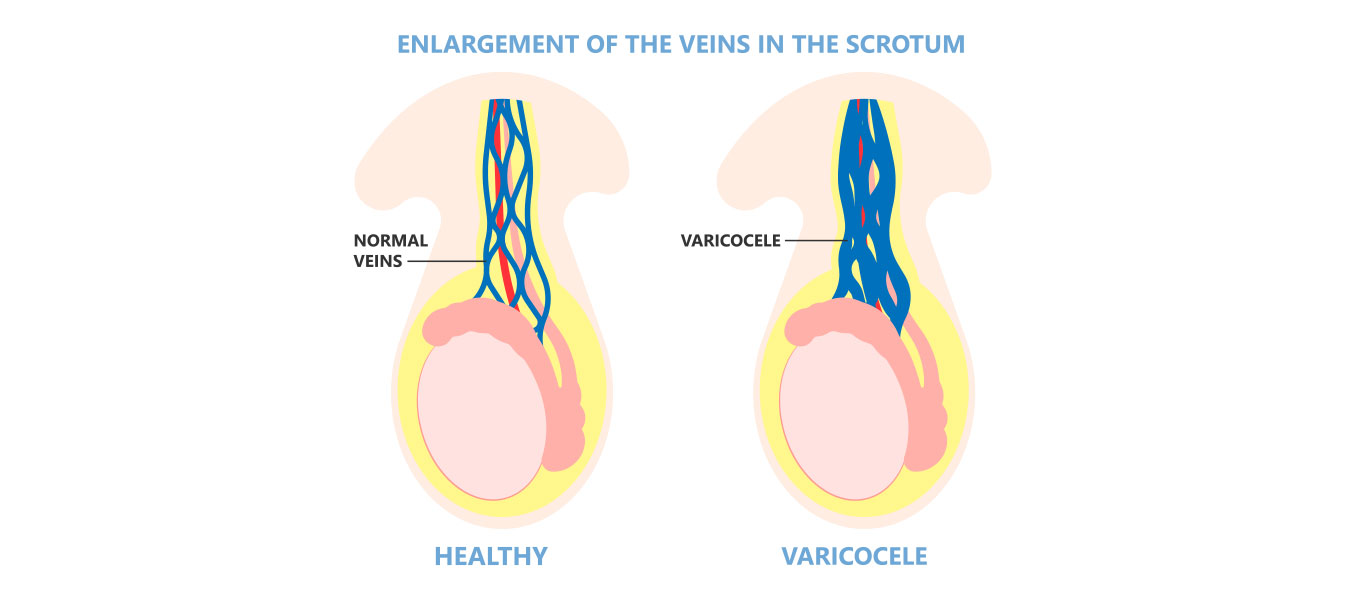
Varicocele is an abnormal enlargement of a group of veins in your scrotum. These veins are similar to varicose veins on the legs. Poorly functioning valves in these veins can cause blood vessels to swell.
When non-surgical varicocele closure is performed
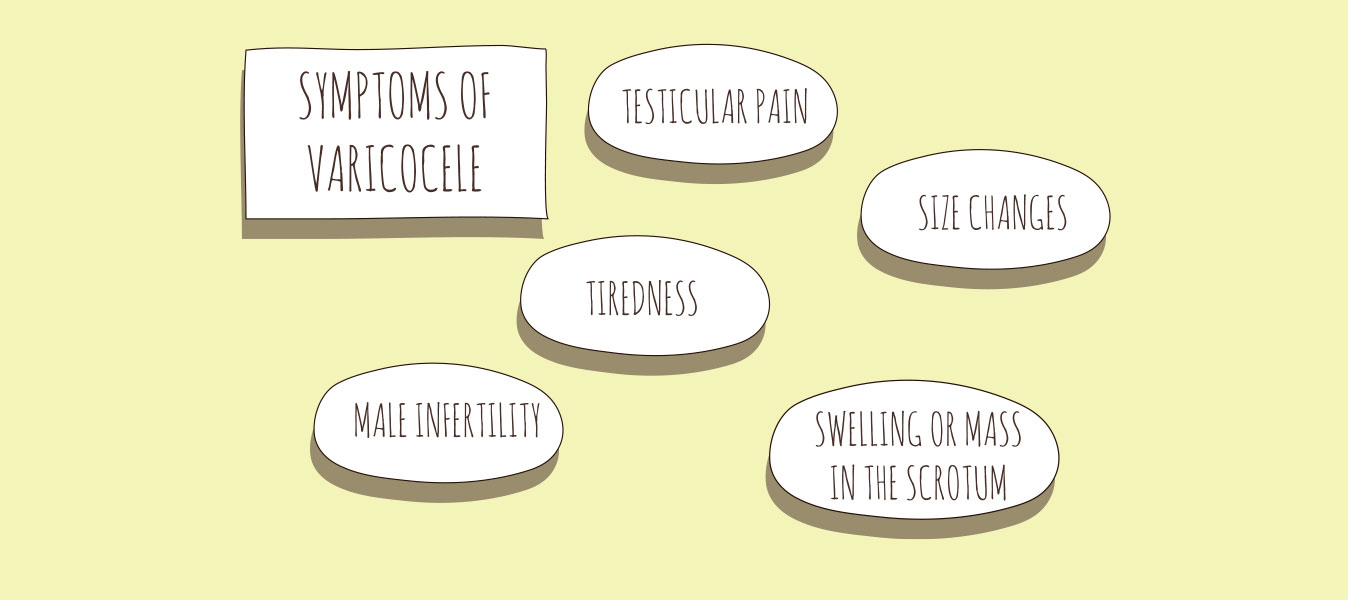
Varicocele usually has no symptoms. In teenagers, they can cause slow testicular growth. They can also cause pain and swelling. And they can also lead to infertility. You may be treated for symptoms or infertility.
Surgery and varicocele embolization are the two main treatments. Both choices have similar success rates. But the recovery time when embolization is performed is usually shorter. This is because only a small catheter and a needle are used. It is also performed under local anesthesia.
Surgery could be a better choice if you have varicocele that affects both testicles. Talk to your doctor about the choice that makes the most sense to you. Varicocele embolization is successfully performed in a specially equipped room in the Pulse Cardiology Center.
Risks of non-surgical treatment of varicocele
The varicocele embolization procedure is safe. Some very rare risks are:
- Infection
- Allergic reaction
- Bleeding
- Coil migration that is sometimes used to block an enlarged vein
- Pain in the lower back
- Inflammation of the scrotum
- Inflammation of the veins
- Nausea
There is also a chance that the procedure will fail. Your varicocele can also come back. This can happen even if the first treatment was successful.
Own risks may vary somewise. They can depend on your age and any other health problems you have. The anatomy of the varicocele can also affect the risk. Be sure to talk to your doctor about any problems before the procedure.
How do I prepare for varicocele embolization?
Our medical team will give you all the information on how to prepare for the varicocele embolization procedure.
Be sure to tell us all about:
- Your medical history
- Any previous problems with allergies, medications or contrast agents
- Any recent symptoms, such as fever
- Any medication you are taking, including over-the-counter medications
If necessary, you should stop smoking beforehand. This will reduce the chance of some complications. Also, do not eat or drink anything for several hours before the procedure. Make sure friends or family members are notified to pick you up after the intervention.
You may need additional tests before the intervention. For example, you will definitely need an ultrasound of the scrotum. It can provide more details about your varicocele.
How is non-surgical varicocele closure performed?
Your doctor will tell you what to expect during varicocele embolization. The procedure can take several hours. In general, you can expect the following:
- You will probably get a medicine for relaxation and sleepiness first.
- Our medical team will closely monitor your heart rate and blood pressure.
- A medical technician will clean the area, ie. that part of the body. The doctor will then insert a needle inside of the thigh to access the main vein. A catheter tube is then inserted into this vein.
- You will receive an injection of a local anesthetic into the area on the inside of your upper leg. You may feel a small sting. An injection with a local anesthetic will prevent you from feeling anything during the procedure.
- X-rays will help the doctor to move the tube to the right place in the scrotum. The doctor may inject contrast material into a vein to improve the visibility of the blood vessels on the X-ray machine. You can feel a little heat.
- The doctor will release a small coil or special fluid into the affected vein. This is called a blocker. It usually redirects blood flow to other nearby veins. Then blood can normally come out of the scrotum. If all goes well, the varicocele will disappear.
- After that, the catheter will be removed. A patch or bandage will be placed over the area of the entrance to the thigh.
What happens after the varicocele embolization procedure?
The staff of the Pulse Cardiology Center will closely monitor you after the procedure of non-surgical closure of the varicocele. In most cases, you will be able to go home the same day. Your doctor will give you the necessary information about how successfully the affected veins have been repaired.
You should rest for the rest of the day after the intervention. The next day you will be able to perform your usual activities. If you have been taking medication to help you relax, you should not drive or make any important decisions for at least 24 hours. You will probably have to wait before you start doing more strenuous activities, such as running. You may need to avoid sexual activity for a few weeks.
Tell your doctor if you have any problems after the procedure. This includes heat and redness at the injection site.
After the procedure, the doctor will write on the report when you need to come for a check-up. Minor pain may occur in patients immediately after the intervention. If you have had problems with infertility, you should, in agreement with your doctor, do a spermogram – sperm analysis. You can check if your fertility has increased. In some cases, it will be necessary to repeat the procedure or surgery if the varicocele returns.
Next steps
Before you agree to an examination or procedure – non-surgical varicocele closure, make sure you know:
- Name of the procedure
- The reason you are undergoing a test or procedure
- What results to expect and what they mean
- Risks and benefits of varicocele embolization
- What are the possible side effects or complications
- When and where to perform the procedure
- Who will perform the procedure and what are the qualifications of that person
- What would happen if you did not undergo varicocele embolization
- Any alternative test or procedure to consider
- When and how you will get results
- Who to call after the intervention if you have questions or problems
- How much you will have to pay for the intervention
