Home » Services » Interventional procedures » Stent insertion
Stent Insertion
Interventional procedures for the treatment of coronary heart disease
Coronary arteries deliver oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle. Over time, plaque can build up in the coronary arteries and restrict blood flow through them. This is known as coronary heart disease. This can damage your heart muscle and put you at risk for a heart attack.
A heart stent is used to treat narrowed or clogged coronary arteries. It can also be used to improve blood flow immediately after a heart attack. A heart stent is an expandable coil made of metal mesh.
Doctor can place a stent during coronary angiography, a non-surgical and minimally invasive procedure. The device is designed to support the walls of the arteries, keep the artery open and improve blood flow in the heart.
According to the experience of experts from the Pulse Cardiology Center, coronary angiography with stents is usually recommended for patients who have only one or two blocked arteries. If you have more than two blocked arteries, cardiac bypass surgery may be a better option for you.
The implantation of the stent in the Pulse Cardiology Center is performed in a specially equipped Cath-lab, and the procedure is performed by eminent experts in cardiology and radiology, subspecialists in interventional cardiology and interventional radiology.
What is a stent?
A stent is a tiny “tube” that your doctor can place in a blocked passage to keep it open. The stent restores the flow of blood or other fluids, depending on where it is placed.
Stents are made of metal or plastic. Stent grafts are larger stents used for larger arteries. They can be made of specialized fabric. Stents can also be coated with drugs to prevent the artery from closing.
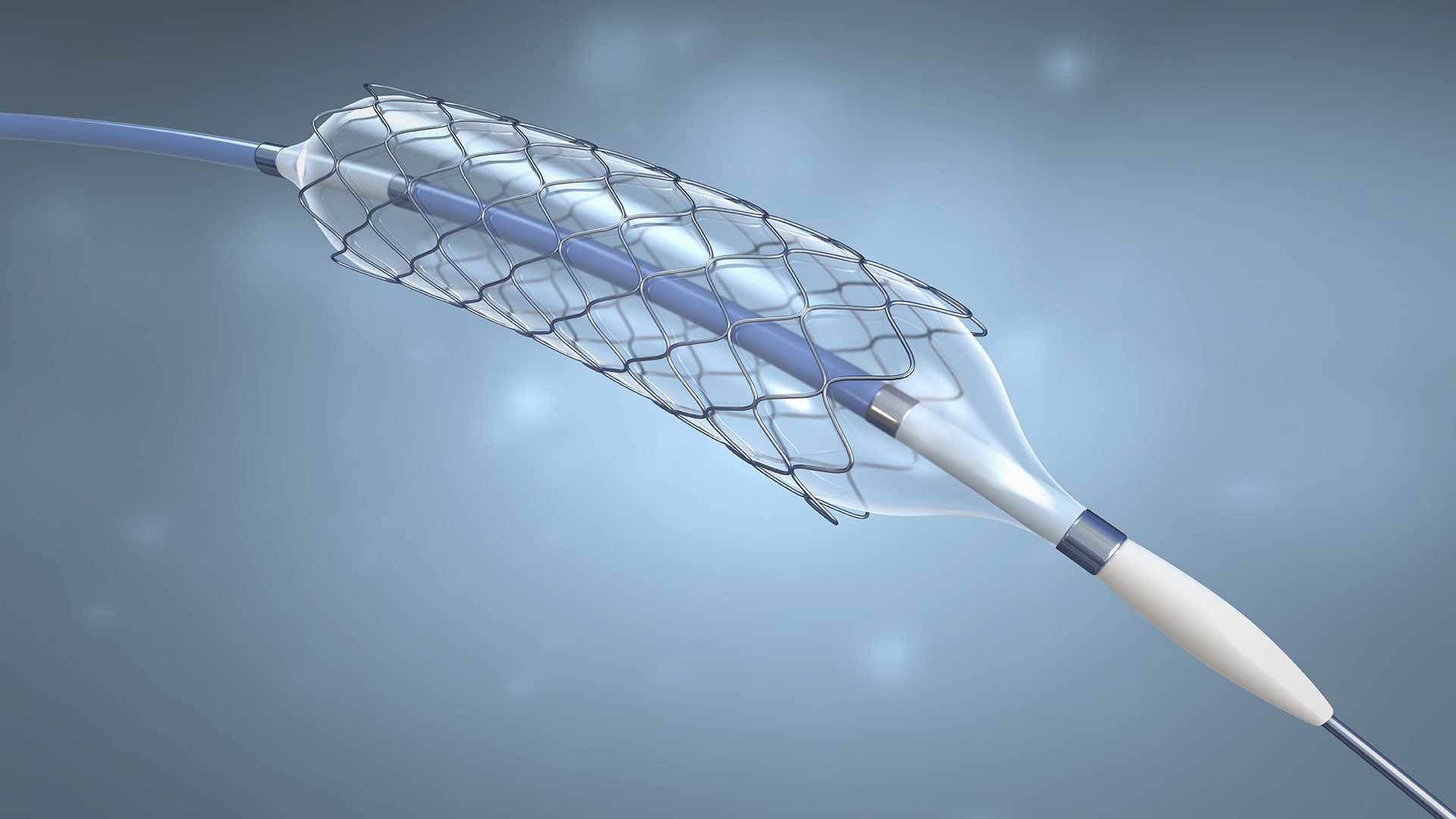
Why and when a coronary heart stent is implanted
Stents are usually needed when plaque blocks a blood vessel. Plaque is made of cholesterol and other substances that accumulate and attach to the walls of blood vessels. You may need a stent during the emergency procedure. An emergency procedure is more common if a heart artery called the coronary artery is blocked. Your doctor will first place a catheter in a blocked coronary artery. This will allow them to do balloon angioplasty to open the blockage. He will then place a stent in the artery to keep the blood vessel open.
A stent can also be useful in preventing aneurysms from rupturing in the brain, aorta, or other blood vessels.
In addition to blood vessels, stents can open any of the following passages:
- bile ducts – tubes that carry bile to and from the digestive organs
- bronchi – small airways in the lungs
- ureters – tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
These passages can be blocked or damaged just as blood vessels can.
How is a heart stent placed?
There are several ways to place a stent.
Doctors usually place a stent using a minimally invasive procedure. The doctor may place a heart stent under local anesthesia. He will make a small incision on the groin, arm or neck and with a special catheter he will guide specialized tools through your blood vessels to reach the area that needs a stent. One of these tools may eventually have a camera that helps the doctor guide the stent and a stent will be inserted at the top. During the procedure, your doctor may also use a imaging technique called an angiogram to guide the stent through a blood vessel.
Your doctor will use special devices and agents (contrasting colors) and monitors to guide the catheter through your blood vessels to a narrowed or clogged coronary artery. When the catheter reaches the narrowed or blocked area, the doctor will inflate the balloon. This will dilate the stent and dilate the artery, allowing increased blood flow. Finally, the doctor will inflate the balloon, remove the catheter and leave the stent in place. The doctor will then remove the instruments from your blood vessels.
During this procedure, the filter will prevent plaque and blood clots from loosening and floating freely in your bloodstream. After the procedure, you will need to take medications that help prevent clotting inside the stent. As your artery begins to heal, your own tissue will begin to connect with the stent mesh, adding strength to your artery.
Sometimes a certain type of stent is used, which is called a drug stent. Such stent is coated with drugs to reduce the risk of restenosis. Restenosis occurs when your artery narrows again.
Stent implantation – preparation
Preparation for stent placement depends on the type of stent used. You usually prepare for a stent that is placed in a blood vessel by taking the following steps:
- Tell your doctor about any medications or supplements you are taking.
- Do not take medicines that make blood clotting difficult, such as aspirin, clopidogrel, ibuprofen and naproxen.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions for any other medicines you should stop taking.
- Quit smoking if you smoke.
- Tell your doctor about any illnesses, including colds or flu.
- Do not drink water or any other liquid the night before the intervention.
- Take all the medicines prescribed by your doctor.
- Come to the hospital at the agreed time to prepare for the intervention.
- Follow any other instructions given to you by your doctor.
- You will receive a local anesthetic at the incision site. You will also receive intravenous medications to help you relax during the procedure.
How long will I stay in the hospital after the stent is implanted
- The usual procedure is to stay in the day hospital after the intervention. This helps us to make sure there are no complications. You may need to stay in the hospital longer if the stent is placed due to coronary problems such as a heart attack or stroke.
- You may feel a slight pain at the incision site through which the catheter is inserted. Mild painkillers generally solve this pain. Your doctor will probably prescribe anticoagulant medication to prevent the blood from clotting.
- When you return home, drink plenty of fluids and limit physical activity for a while. Be sure to follow all doctor’s instructions.
Heart stent implantation – advantages
For many people, stenting has a positive impact on quality of life. The combination of coronary angiography and stenting can be a lifesaver, especially when performed immediately after a heart attack. Stent implantation can significantly improve blood flow and prevent further damage to the heart muscle. It can also improve the symptoms of heart disease, such as chest pain (angina) and difficulty breathing. In many cases, you will feel the benefits immediately.
In some cases, stenting can eliminate your need for coronary bypass surgery. Stenting is much less invasive than bypass surgery. Recovery time is also much shorter. It only takes a few days for the patient to recover from the stent implant, while it may take six weeks or longer for you to recover from the bypass surgery.
Whether you are a candidate for stenting or not depends on many factors, including the number of arteries that are blocked and other health assessments.
What are the risks and complications of a heart stent?
As with many medical procedures, you may experience an allergic reaction to medications or materials used for coronary angiography and stenting. This procedure can also cause bleeding, damage to blood vessels or the heart, or irregular heartbeat. Other potential but rare complications include heart attack, kidney failure and stroke.
After the procedure, scar tissue can form inside your stent. If this happens, another procedure may be needed to remove it. There is also a risk of blood clots forming in your stent. You will need to take medication to prevent this. Report to your doctor immediately if you experience any chest pain.
Stent implantation and complications
Any surgical procedure carries risks. Stent placement may require access to the arteries of the heart or brain. This leads to an increased risk of side effects.
Risks associated with the stent include:
- an allergic reaction to drugs or contrast materials used in the procedure
- breathing problems due to anesthesia or the use of a stent in the bronchi
- bleeding
- artery blockage
- blood clots
- heart attack
- blood vessel infection
- re-narrowing of the artery
Very few complications have been reported with stents, but there is little chance that the body will reject the stent. You should discuss this risk with your doctor. Stents have metal components, and some people are allergic or sensitive to metals. Stent manufacturers recommend that if someone has a sensitivity to metal, they should not be subjected to stent implantation. Talk to your doctor for more information. Our team can provide you with the latest information regarding your condition and potential problems.
It is more commonly thought that the risk of not getting a stent is not greater than the risks associated with stent implantation. Restricted blood flow or clogged blood vessels can have serious and deadly consequences.
How to behave after stent implantation
Although stenting can result in significant improvement, it is not a cure for heart disease. You still need to address the contributing factors, such as high cholesterol, high blood pressure and being overweight. Your doctor may prescribe medication or other treatments to help you solve these problems. I can also encourage you to:
- Eat healthy
- Exercise regularly
- Quit smoking
Taking steps to control cholesterol and blood pressure and lead a healthy lifestyle can help you treat and prevent heart disease.
50% of heart attacks occur in people with normal cholesterol
Check the level of cholesterol and plaque in the blood vessels with the help of non-invasive scan diagnostics. CT coronary angiography, CT angiography or coronary calcium assessment are procedures that provide information about the condition of your blood vessels in a fast, efficient and painless way.
Stent insertion at the Pulse Cardiology Center
Stent insertion is performed in a specially equipped Cath-lab by experts in interventional cardiology and radiology. Take a look at our team and schedule an appointment. Our call center is available every day until 8 pm on 0117555000 if you have additional questions. You can also contact us via email: info@pulskardioloskicentar.rs
The cost of stent insertion
Coronarography with 1 stent implanted price – 250.000 din.
Each subsequent stent implanted price – 95.000 din.
