Home » Services » CT Scanner » CT coronarography
CT Coronarography
Cardiovascular diseases (CVD), diseases of the heart and blood vessels, are the leading cause of death in the world and in Serbia.
Over 17 million people die from cardiovascular diseases every year, 85% of these deaths are due to acute myocardial infarction or stroke.
Cardiovascular diseases include:
- Coronary heart disease – a disease of the arteries that feed the heart muscle
- Cerebrovascular diseases – a disease of the blood vessels that supply the brain with blood
- Peripheral arterial disease – a disease of the blood vessels that supplies blood to the upper and lower extremities (arms and legs)
- Rheumatic heart disease – damage to the heart muscle and heart valves due to rheumatic fever caused by bacteria (Streptococcal bacteria)
- Congenital heart disease – heart malformations present at birth
- Deep venous thrombosis and pulmonary thromboembolism – blood clots in the veins of the lower extremities that dislocate and reach the heart and lungs through the bloodstream
- Heart attack or stroke – usually occurs due to complete blockage of the blood vessel responsible for supplying part of the heart muscle or part of the brain. A stroke can also be caused by a ruptured blood vessel and consequent bleeding in the brain, or by a blood clot clogging a blood clot.
What is coronarography?
Coronary angiography is an examination that uses intravenous iodine contrast and a CT scan to examine the arteries that supply blood to the heart muscle and determine if they are narrowed. Images generated during a CT scan can be reshaped to create three-dimensional (3D) images that can be viewed on a monitor.
Coronary angiography is a method of imaging the coronary arteries that helps determine if plaque buildup has narrowed the coronary arteries. Plaque is made of various substances such as fat, cholesterol and calcium that accumulate along the inner lining of the arteries.
Plaque, which builds up over time, can reduce or in some cases completely block blood flow. Patients undergoing coronary angiography receive iodine-containing contrast material as an intravenous (IV) injection to ensure the best possible images of the blood vessels of the heart.
Computed tomography, better known as CT, is a diagnostic method of the heart blood vessels imaging. Like traditional X-rays, it creates multiple images or images of the inside of the body. Cross-sectional images generated during CT scanning can be reshaped into multiple planes. They can even generate three-dimensional images. These images can be viewed on a computer monitor, printed on film or a 3D printer, or transferred to a CD or DVD. CT images of internal organs, bones, soft tissue and blood vessels provide more detail than traditional X-rays, especially soft tissues and blood vessels.
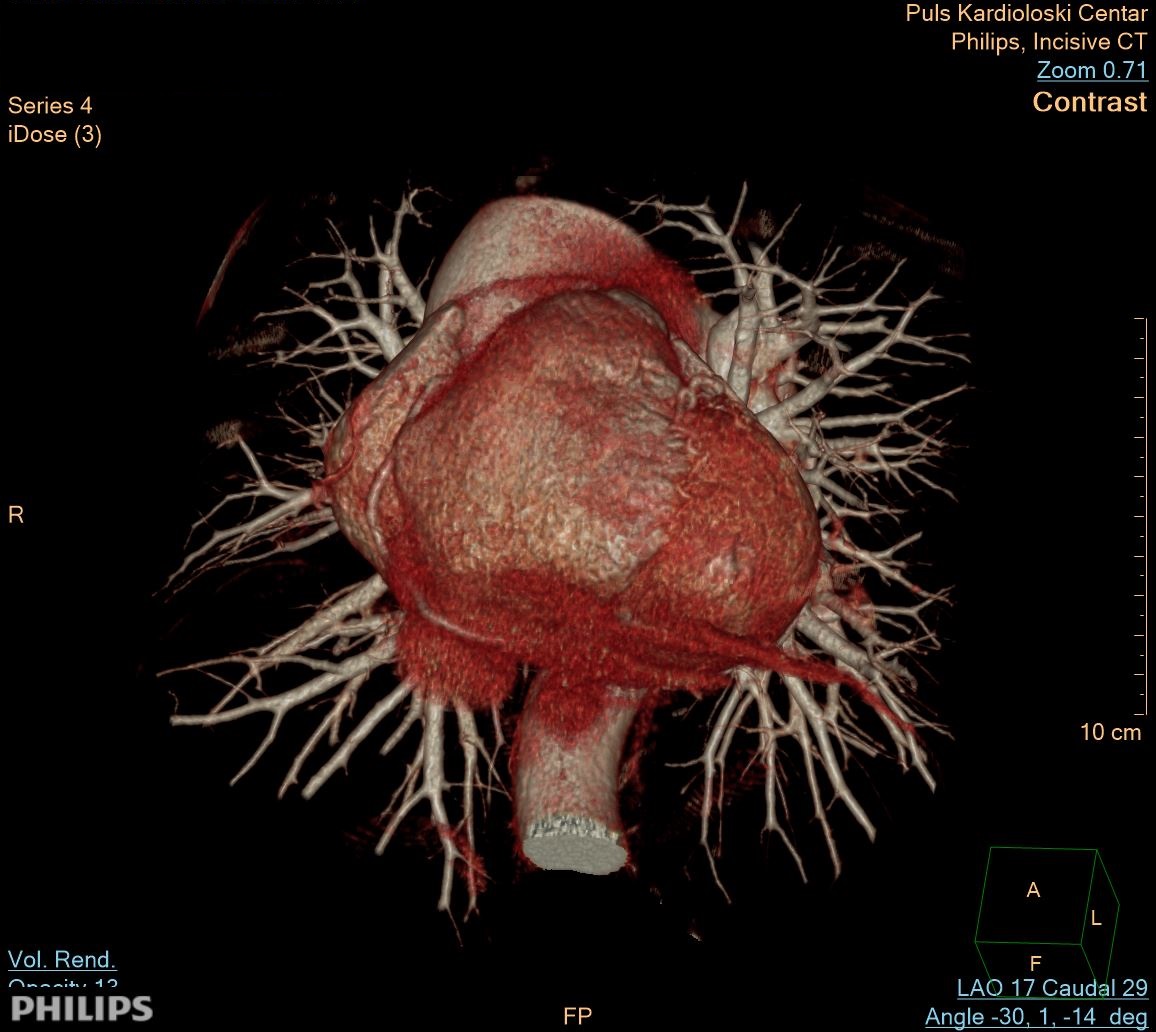
When to performe CT coronaography
Many doctors recommend CT coronary angiography for patients who have:
- Suspicion to abnormal anatomy of the coronary arteries
- low or medium risk for coronary artery disease, including patients with chest pain and normal, non-diagnostic or unclear laboratory and ECG test results
- atypical chest pain with low to medium risk for emergencies
- chronic chest pain
- worsening of symptoms with a previous normal stress test result
- unclear or failed stress test results
- newly formed heart failure with reduced heart function and low or medium risk of coronary artery disease.
- moderate risk of coronary artery disease before non-coronary cardiac surgery
- By-pass of the coronary arteries
For patients who meet the above indications, CT coronary angiography can provide important information about the presence and extent of plaque in the coronary arteries.
In addition to identifying narrowing of the coronary artery as a cause of chest discomfort, it can detect other possible causes of symptoms, such as pulmonary atelectasis, blood clots in the vessels leading to the lungs, or aortic abnormalities. The primary care physician or cardiologist, in consultation with the radiologist who would perform the test, will determine if CT coronary angiography is the appropriate method for you.
Who interprets the results of CT coronarography
A radiologist, a doctor specially trained to monitor and interpret radiological examinations, will analyze the images. The radiologist will send an official report to the doctor who ordered the examination. If you have active chest pain, the radiologist will report the preliminary result immediately. Additional tests may be needed. If so, your doctor will explain why.
Sometimes a follow-up examination is performed because the potential abnormality needs to be further assessed with additional imaging or a special imaging technique. A follow-up inspection may also be performed to determine if there has been any change in the irregularity over time. Check-ups are sometimes the best way to determine if treatment is working or if the abnormality is stable or has changed.
What are the benefits of coronary angiography?
The advantage of CT coronarography is noninvasiveness. An alternative test, cardiac catheterization using a coronary angiogram, is invasive. Catheterization has several complications associated with the placement of a long catheter in the groin or artery of the joint that extends all the way to the heart and the movement of the catheter in the blood vessels. Invasive catheterization requires more time for the patient to recover.
The main advantage of CT scanning is that it can see bones, soft tissues and blood vessels at the same time. For this reason, a CT scanner is suitable for identifying other reasons for your discomfort, such as aortic injury or a blood clot in the pulmonary arteries.
Unlike conventional X-ray CT scan:
- gives very detailed images of many types of tissues
- diagnostic is quick and easy
- has proven cost-effective for a wide range of medical problems
- is less sensitive to the patient’s movement than magnetic resonance imaging – MRI
- can be done if you have a built-in medical device of any type, unlike an MRI
- after CT examination, no radiation remains in the patient’s body.
- X-rays used in CT scans should not have side effects
It is important to tell your doctor before CT coronarography:
If you are pregnant or suspect you may be pregnant
If you are allergic to iodine or have other allergies
If you have kidney disease
If you are diabetic or are being treated for other chronic diseases
Price of the coronary angiography
Price of the MSCT coronary angiography & abdominal artery angiography is 39.900 dinars.
Price of the MSCT coronary angiography & thoracic aortha angiography is 39.900 dinars.
Price of the MSCT coronary angiography & abdominal and thoracic aortha angiography is 45.200 dinars.
