Stroke Center
Stroke is the third leading cause of death in the world and the leading cause of adult disability, but most people do not even know they are in danger. Many do not understand the prevalence of the disease nor do they understand the risk factors for stroke.
In Serbia, every 15 minutes someone experiences, and every 60 minutes someone dies from a stroke who is not chosing neither time or place to hit.
The Stroke Center within the Pulse Cardiology Center was formed to increase public awareness of stroke, its risk factors and warning signs.
In addition to the educational nature, the Pulse Cardiology Center within the Stroke Center focuses on clinical efforts to reduce the time required to diagnose a stroke and be more aggressive in treating stroke and its consequences using various diagnostic tools and tests. At the head of our team is a neurologist with decades of experience, MD Predrag Stanarcevic.
Estimates by various cardiovascular associations are such that 75% of strokes could be prevented or delayed by managing or eliminating risk factors.
Risk factors for stroke
In some cases, there may not be a clear reason why you had a stroke. However, in most cases, we can identify at least one risk factor for stroke. A risk factor is something that puts you at higher risk of having a stroke.
Risk factors for the development of stroke can be divided into two types:
- Modified risk factor: something that can be changed or treated.
- Risk factor that cannot be changed: Something that cannot be changed or treated.
(increasing age, sex, heredity and race, history of previous stroke, blood vessel abnormalities eg aneurysm)
Most common risk factors:
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- Heart disease
- Carotid artery disease
- Smoking
- Family history of stroke
- Previous stroke or transient ischemic attack (TIA)
- High cholesterol
- Obesity
- Inactivity
- Constant consumption of alcohol and various drugs
Another cause for concern is the fact that almost half of all deaths from stroke occur before a person arrives at the hospital. The most likely reason is that many people do not recognize the signs and symptoms of a stroke. Research shows that only half of the respondents recognized sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arms or legs as a warning sign of a stroke.
Warning signs for stroke for women and men
- Sudden numbness or weakness of the face, arms or legs, especially on one side of the body
- Sudden confusion, speech or comprehension problems
- Sudden vision problems in one or both eyes
- Sudden dizziness, loss of balance or coordination, or difficulty walking
- Sudden severe headache with no known cause
The warning signs that women sometimes experience include SUDDENLY:
- pain in the face and limbs
- hiccups
- nausea
- general weakness
- chest pain
- shortness of breath
- palpitations
Click here to see a video on the importance of providing quick help if you think you or a loved one is having a stroke.
If you or a family member has any of these symptoms, call 194 and go to the emergency room.
The most effective stroke treatments are only available if the stroke is recognized and diagnosed within the first three hours of the first symptoms, so keep in mind the time when any symptom first appears.
Pulse Cardiology Center within the Center for Stroke examines a large number of patients with stroke through the advanced treatment of rapid diagnostics in our day hospital, which in addition to diagnostics also provides specialized medical care.
What is a stroke
A stroke is otherwise called a cerebrovascular stroke. Stroke is an emergency in medicine because it can lead to permanent damage or death of a person. Therefore, it is necessary to call a doctor immediately within the first three hours of recognizing the symptoms of a stroke. Symptoms of a stroke can be: confusion or a sudden change in state of consciousness, deprivation (paralysis), weakness or numbness of one side of the body, difficult or disabled speech, sudden severe headache, vision loss, “double images”, loss of balance or dizziness. These are all symptoms that must be an alarm that a stroke may have occurred.
Stroke occurs due to damage to the blood vessels of the brain, which makes it difficult or completely impossible to supply that part of the brain with oxygen and nutrients. When the blood supply to an area of the brain is cut off, the brain cells lose oxygen and die.
There are two types of stroke: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
Types of stroke
Hemorrhagic stroke, in which brain damage occurs due to bleeding in the brain. This happens when a blood vessel ruptures leading to a blood leak. 20% of strokes are hemorrhagic.
There are two types of hemorrhagic stroke:
- Intracerebral hemorrhage (ICH) when blood leaks into brain tissue. It is most often caused by high blood pressure.
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) when blood leaks between the layers around the brain, called the subarachnoid space. It is most often caused by a ruptured aneurysm.
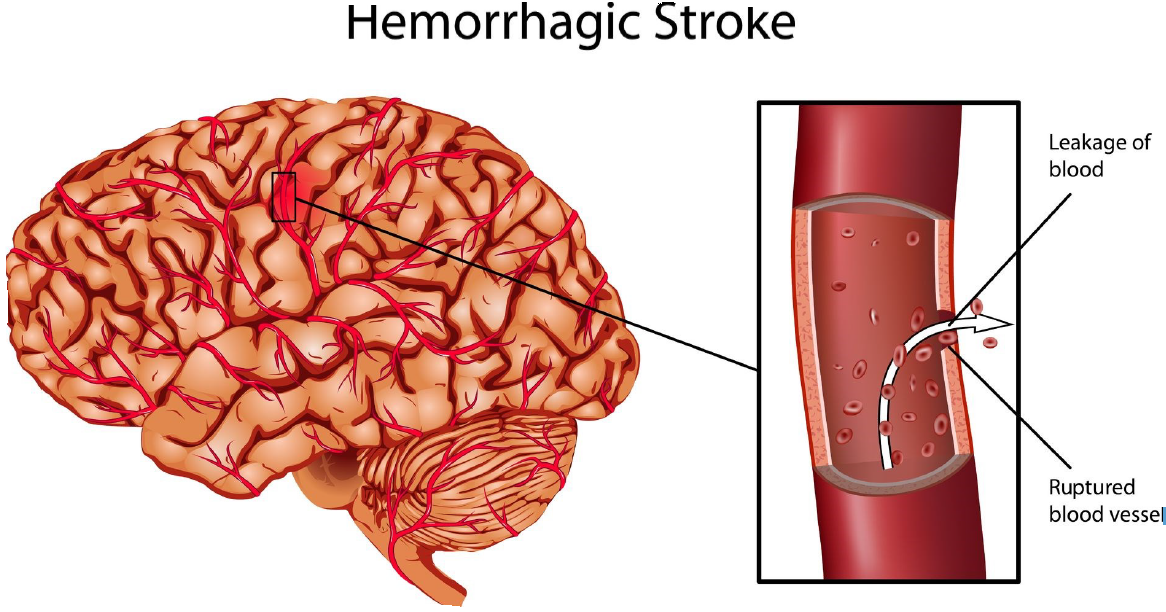
Treatment of hemorrhagic stroke
Examination:
After a hemorrhagic stroke, measures are taken to ensure that your vital signs are stable. You may be given medication to control your blood pressure. They are usually given intravenously to begin with. You may be given medication or a blood transfusion to help the blood clotting. They are also given intravenously. The care team will carefully assess your neurological status during your stay in the day hospital. This includes tests of strength, speech, understanding, feelings and reflexes. You will also be closely monitored for signs of increased pressure on the brain. These signs include restlessness, confusion, difficulty in carrying out orders, and headaches.
Will surgery be needed for my stroke?
In some cases, surgery may be needed to drain or remove blood in or around the brain.
If the aneurysm is the cause of a stroke, a procedure can be taken to prevent re-bleeding. This procedure can be winding or cutting. The winding procedure fills the aneurysm with soft metal spools or mesh to block it and stop or prevent bleeding. The excision procedure places a small metal button around the bottom of the aneurysm to stop or prevent bleeding.
If an abnormality in your blood vessel is found, such as an arteriovenous malformation (AVM), surgery may be needed to stop or prevent the bleeding.
If a serious, life-threatening brain swelling occurs as a result of a stroke, the medical team may discuss the possibility of a surgical procedure called a decompressive craniectomy to relieve the pressure in the brain.
Ischemic stroke which occurs due to the gradual blockage of a blood vessel or due to atherosclerosis or the maturation of a thrombus, which clogs it. 80% of strokes are ischemic.
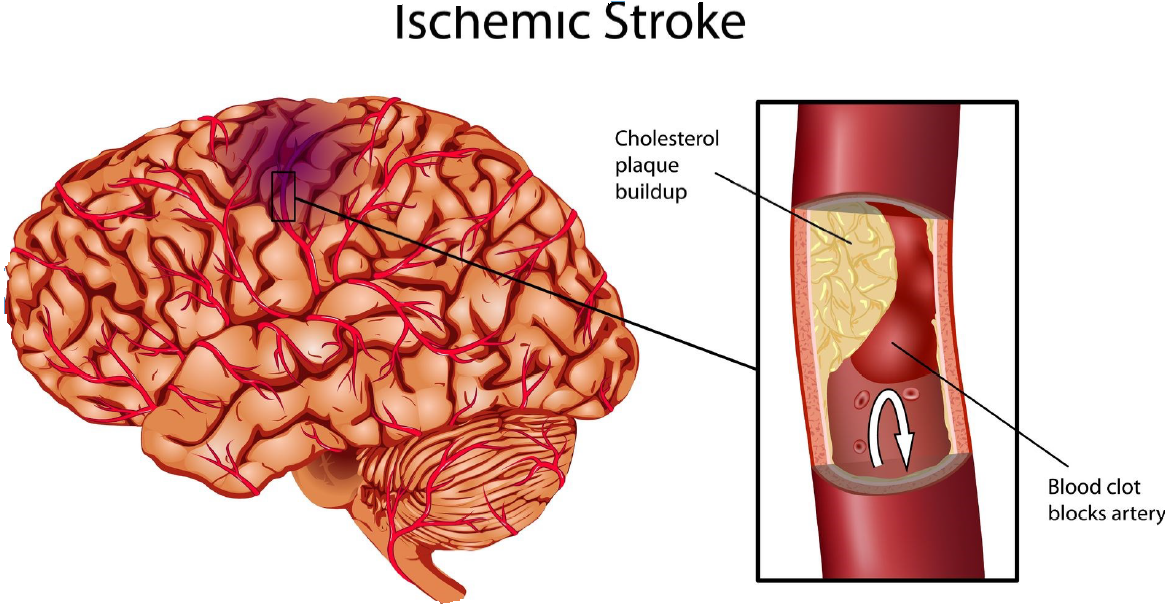
A temporary ischemic attack (TIA) is also called a “mini-stroke” because the blockade is temporary. It does not cause permanent brain damage. Although not a stroke, a TIA is an important warning sign that you risk a stroke in the future.
Treatment of ischemic stroke
Examination:
After an ischemic stroke, measures will be taken to ensure that your vital signs are stable. Our team will carefully assess your neurological status during your stay in the day hospital. This includes tests of strength, speech, understanding, feelings and reflexes.
You will also be closely monitored for signs of increased pressure on the brain. These signs include restlessness, confusion, difficulty in carrying out orders, and headaches.
During your stay in the day hospital, our team will work on identifying and treating your variable risk factors. This may include medication and education about lifestyle changes. This will help prevent stroke in the future.
Will surgery be needed for my stroke?
In most cases, surgery will not be needed for an ischemic stroke.
If you have a severe blockage in one or both carotid arteries in your neck, you may need surgery to repair it. During this operation, the surgeon removes the accumulated plaque near the carotid artery. If a serious, life-threatening swelling of the brain occurs as a result of a stroke, the doctor may suggest a surgical procedure called a decompressive craniectomy to relieve the pressure in the brain.
Which part of the brain is affected by a stroke
After a stroke, the affected part of the brain stops functioning and neurological outbursts occur. The symptoms you see in a stroke depend on the area of the brain that is damaged.
Right hemisphere of the brain
- Feels and moves the left side of the body
- Controls emotions
- Organizes
- Track time
- Pays attention to the left side of the space
Left hemisphere of the brain
- Feels and moves the right side of the body
- Controls speech
- Understands language
- Reads, writes, does math
- Remember words
Cerebellum
- Keeps movement smooth and balanced
Spinal cord
- Controls and regulates basic bodily functions such as heart rate,
- Breathing, swallowing and blinking
- Controls alertness
- Focuses attention
Diagnostic tests for stroke
It may be necessary to do several different types of tests and analyzes if doctor suspects that you had a stroke. These tests can be performed for a variety of reasons. Here are the most common tests that can be done for both ischemic and hemorrhagic strokes.
Tests that can be done to find out what kind of stroke you had:
- CT scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
Tests that could be done to give us more information about the type of stroke or help us determine why you had a stroke:
- Carotid Doppler
- Echocardiogram
- Heart monitoring
- Cerebral angiogram
- CT angiogram (CTA)
- MRI angiogram (MRA) or Venogram (MRV)
- Blood tests
Tests that can be performed to monitor other conditions:
- Electroencephalogram (EEG)
- Peripheral or transcranial Doppler
- Blood tests
At the Pulse Cardiology Center, there is a specially formed package for examining the etiology of stroke, which includes:
- Neurologist Examination
- Doppler of blood vessels of the neck
- TCD
- Basic heart examination
- Holter TA
- Holter ECG
- Laboratory analyzes
- Vascular Surgeon Examination
- CT of the head
PACKAGE PRICE: 56.000 dinars
Several centers of excellence have been established within the Pulse Cardiology Center. You can get more information about our Centers by clicking on the links:
