Dr. Slobodan Ćulafić – neuroradiologist, is our leading expert in performing endovascular procedures on the carotid artery, aorta, brain aneurysms, and spinal blocks for pain management.
What are carotids?
Carotids or carotid arteries have a very important role, they pass oxygen-rich blood from the heart to the head and cerebrum. The cerebrum is responsible for speech, thinking, personality, and motor and sensory functions.
The blood vessels of the brain must be passable in order for its functions to be preserved. Any blockage of blood vessels in the neck requires treatment, and what will be used in the treatment depends on the severity of the picture.
How does carotid artery disease occur?
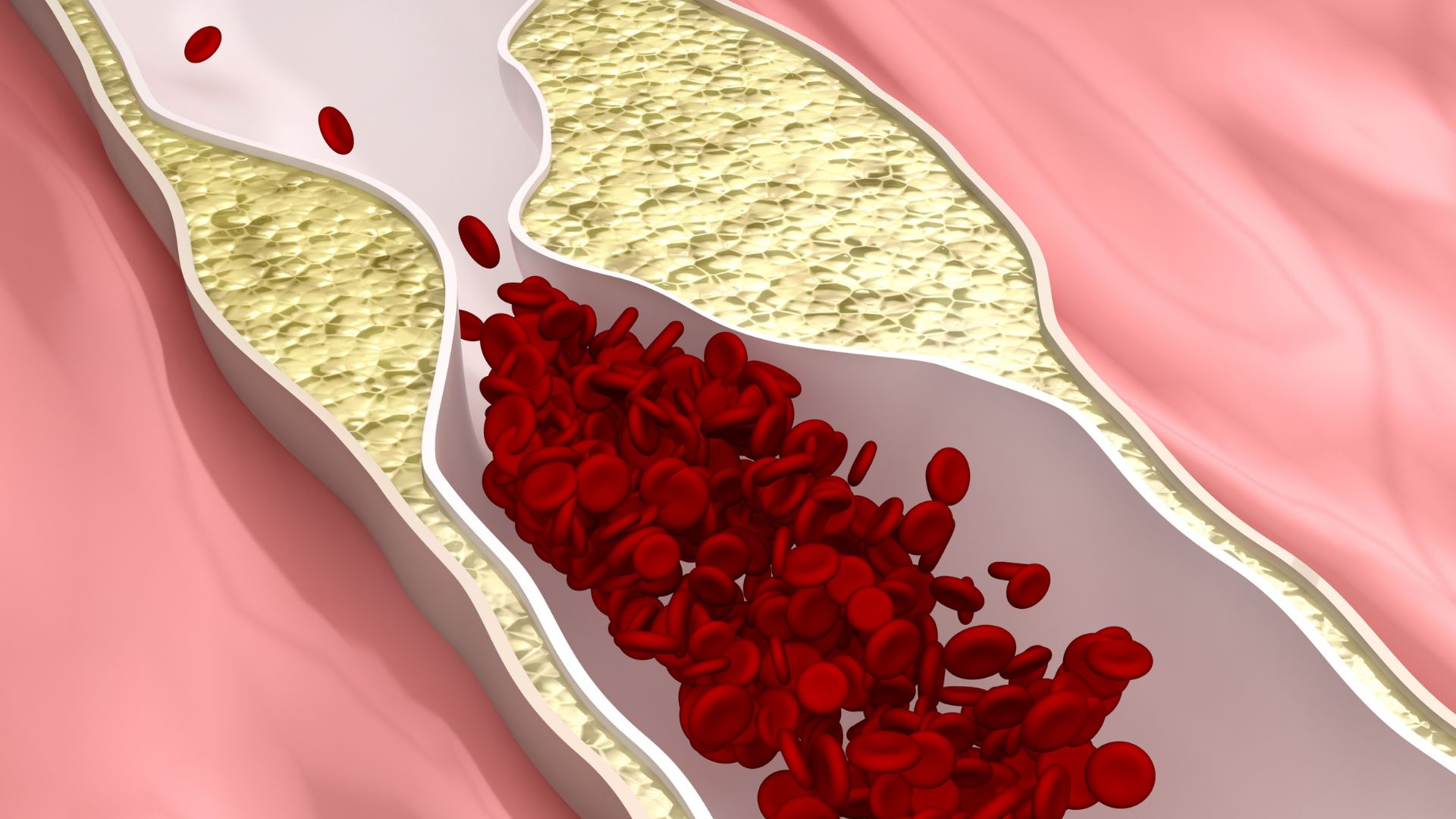
The disease of the carotid arteries is also called stenosis and implies the occurrence of narrowing in the arteries and a reduction in the flow of fresh blood through the arteries. The most common reason for the narrowing of the carotid arteries is atherosclerosis, that is, the accumulation of plaque on the walls of the blood vessels.
Plaque is formed when substances such as fats, cholesterol, calcium, proteins and other waste cellular substances accumulate on the walls of blood vessels.
When the amount of plaque increases, it can partially or completely close a blood vessel, and in this case an artery, after which blood flow to certain tissues stops. Tissues without fresh blood and oxygen quickly begin to die and the consequences are difficult to repair. In this way, a stroke occurs due to carotid blockage.
Blockage of the carotid artery and stroke can also occur due to the arrival of a thrombus or due to the breaking off of part of the plaque from the walls of blood vessels, which, like a thrombus, can block a blood vessel.
In addition to carotid-related situations, a stroke can also occur due to a ruptured aneurysm. At the Pulse Cardiology Center, we have established a stroke center that is focused on reducing the time required for stroke diagnosis and more aggressive treatment of stroke and its consequences.
Symptoms of carotid artery disease
As with most cardiovascular diseases, the symptoms of this disease are often absent in the beginning, so it may happen that the patient does not even know that he has a problem until he has a stroke or a temporary ischemic attack.
A transient ischemic attack or TIA (transient ischemic attack) or mini-stroke is a sure sign that the danger of a stroke exists and that the probability is high. So if this attack happens to you or someone you know, you need to act.
You will recognize a mini-stroke by the following symptoms:
- sudden loss of vision
- sudden weakness
- sudden numbness of one side of the body, one arm, one part of the face
- difficulties in understanding, speaking, communication in general
- coordination problems
- confusion
- dizziness
- difficulty swallowing
A TIA requires immediate medical attention. It is impossible to know exactly when a stroke will occur after this attack, and that is why it is important to react and treat the problem immediately.
People who have experienced an immediate ischemic attack are at a much higher risk of having a stroke, numerically, the probability is 10 times higher than in other people.
Risk factors for the development of carotid disease
It is possible to enumerate the factors that increase the possibility of developing carotid disease:
- genetics – if there are members in the family who have been diagnosed with atherosclerosis somewhere in the blood vessels, there is a greater chance that the problem will occur in other members as well.
- years of life – age significantly increases the possibility of developing carotid problems. Before the age of 75, men are at greater risk, while after 75, women are.
- hyperlipidemia – elevated fats, cholesterol and triglycerides also increase the chance of plaque clogging blood vessels.
- smoking
- hypertension
- diabetes
- overweight
- lack of physical activity
Usually, problems with the accumulation of plaque first appear in the coronary arteries, and after a few years in the carotid arteries.
How is carotid artery disease diagnosed?
There are several ways in which it is possible to diagnose the blockage of blood vessels of the neck:
- Carotid color Doppler – this is a non-invasive, painless method of ultrasound imaging of the carotid arteries, and due to its reliability and practically no contraindications, it is one of the most commonly used methods for this purpose.
- Carotid angiography – unlike carotid doppler, this method is invasive because the catheter is introduced into a blood vessel on the leg or arm and is moved all the way to the carotid, while the movement is monitored with a special X-ray machine. This method involves the use of a contrast material that is passed through the blood vessel to register the narrowing.
- Computed tomography (CT) of the brain – recommended in situations where a stroke or temporary ischemic attack is suspected, but also when a stroke or attack has already occurred. Ct scanning involves the use of higher intensity X-rays, which are used to obtain precise images of the brain. If necessary, contrast is injected into the vein to increase the quality of the image.
Thanks to CT, it is possible to see the damage that occurred in the brain after a stroke.
- CT angiogram (CTA) – this method allows obtaining high-quality, precise 3D images of the carotid artery because it uses advanced CT technology and intravenous contrast.
- Magnetic resonance angiogram (MRA) – using a magnetic field and radio waves, precise images of the carotid and vertebral arteries are obtained.
Depending on the condition of the patient and the stage of the disease, the choice of method for diagnosing carotid disease will also depend.
How is carotid blockage treated?
The good news is that it is possible to treat the blockage of blood vessels in the neck and to a large extent successfully.
In the best situations, when the problem, i.e. the accumulation of plaque, is detected in time, lifestyle changes and regular therapy prescribed by experts can be sufficient. In the later stages, the options change, but there is still hope for improvements in the patient’s situation.
We will refer to the two most common interventions: surgery and endovascular treatment.
Carotid artery surgery
Traditional carotid surgery or endarterectomy is recommended for symptomatic patients when the plaque level is over 50% and for asymptomatic patients when the occlusion level is over 60%.
This method involves opening the carotid artery where the plaque has accumulated and cleaning it. During the intervention, the patient is under total or local anesthesia. When the cleaning is complete, the surgeon closes the site through which he accessed the blood vessel and the blood continues to flow normally through this blood vessel.
Endovascular treatment of carotid arteries
This treatment is a very good way to solve problems with blocked carotid arteries, even in high-risk patients. The procedure is minimally invasive, because the carotid artery is not opened, but a thin catheter is inserted into the vein and led all the way to the artery and the site of blockage.
All the time, the procedure is monitored by X-ray. When the instruments are brought to the right point, the balloon is inflated, which opens the artery, and the embolic protection device collects the debris, so that a part does not break off and cause a blockage elsewhere. After that, a stent is placed, which remains permanently in place and enables unhindered blood flow.
We are proud to say that this procedure can be done in our institution. Specialists with extensive experience in the treatment of vascular problems, led by MD Slobodan Ćulafić – neuroradiologist, are waiting for you.
Which treatment method has more advantages?
Endovascular treatment does not require total anesthesia, the patient is awake and sedated, recovery is faster and there is no scar on the neck, because in this way the carotid artery is not accessed, but through a vein.
After two weeks, the patient can return to daily activities. Classic surgery also does not require a long stay in the hospital, but it is a more invasive method and the recovery is a little slower.
If you recognize symptoms that may indicate carotid problems or simply want to act preventively, make an appointment with our experts. They are there to provide you with an insight into the state of your blood vessels and suggest ways of treatment if you need it.