Otorhinolaryngology
It’s not just chronic sinus problems or hearing loss that will lead you to see an otorhinolaryngology (ENT) specialist. This branch of medicine studies all diseases and conditions of the ear, nose, and throat, which play key roles in the body’s daily functioning.
Otorhinolaryngologists are experts in diagnosing and treating a wide range of ear, nose, and throat diseases, including:
- Ear (otology): infections, hearing loss, tinnitus, balance disorders, eardrum damage, and ear canal tumors.
- Nose (rhinology): allergies, sinusitis, polyps, deviated septum, nosebleeds, and breathing problems.
- Throat (laryngology): throat infections, hoarseness, swallowing problems, gastroesophageal reflux, vocal cord polyps, and throat tumors.
An ENT examination allows specialists to determine the exact cause of symptoms related to the ear, nose, or throat, make an accurate diagnosis, and recommend appropriate therapy. These examinations are crucial to prevent complications and long-term problems that can arise from untreated conditions. Regular ENT check-ups are especially important for patients with chronic issues or those frequently exposed to infections or allergies.
When do you need an ENT examination?
If you are experiencing any of the following symptoms, it is recommended to schedule an appointment with an ENT specialist as soon as possible:
- Hearing loss or ringing in the ears (tinnitus)
- Ear pain or recurring ear infections
- Sinus problems, such as a blocked nose or frequent sinus infections (sinusitis)
- Changes in voice, such as hoarseness or loss of voice
- Balance disorders or dizziness
- Unexplained nosebleeds
- Difficulty swallowing or feeling of a lump in the throat
- Changes in the color or texture of the skin on the face, neck, or ears
A timely ENT examination and diagnosis can significantly improve treatment outcomes, reduce the risk of complications, and ensure faster recovery.
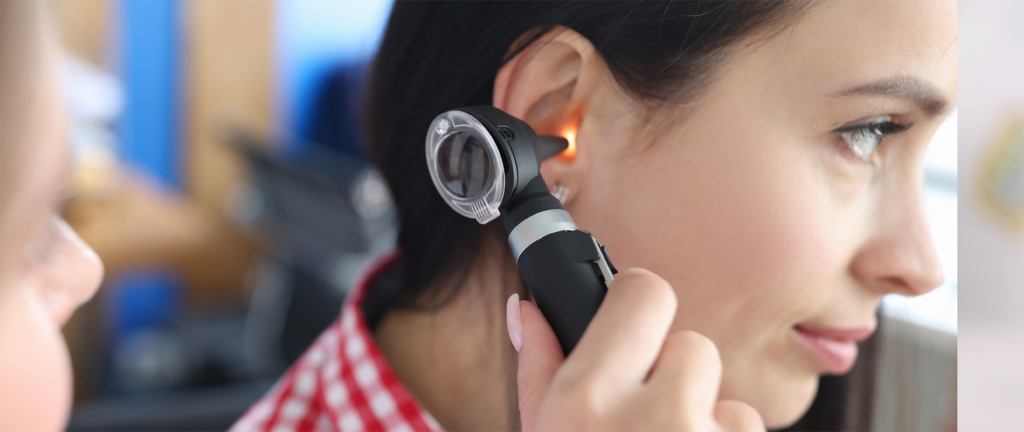

Common diseases treated by an ENT specialist
ENT specialists frequently encounter a wide range of diseases affecting the ear, nose, and throat. Some of the most common conditions include:
Sinusitis
Sinusitis can be acute or chronic. Symptoms include pain in the forehead and cheeks, a blocked nose, difficulty breathing, nasal discharge, and sometimes loss of the sense of smell. Untreated sinusitis can lead to serious complications, such as infections in nearby structures (eyes, brain).
Otitis (ear infection)
Infections can affect the outer, middle, or inner ear. Outer ear infections (otitis externa) are commonly known as swimmer’s ear, while middle ear infections (otitis media) are common in children and often accompanied by pain, hearing loss, and fever. Inner ear infections (labyrinthitis) can cause dizziness and balance problems.
Vocal cord issues
Vocal cord polyps, hoarseness, loss of voice, or speech difficulties may be signs of more serious conditions such as benign polyps, cysts, or even vocal cord cancer. Some changes require surgical intervention or speech therapy (logopedics).
Allergic rhinitis
Inflammation of the nasal mucosa caused by allergies. Symptoms include sneezing, nasal itching, runny nose, and congestion. These conditions can significantly affect quality of life, and untreated allergic rhinitis can increase the risk of developing sinusitis.
Tonsillitis
Tonsillitis can be acute or chronic. Symptoms include a sore throat, difficulty swallowing, fever, and swollen tonsils. In some cases, recurrent infections may require surgery (tonsillectomy).
Pharyngitis
Inflammation of the pharynx can be caused by viruses or bacteria. Symptoms include a sore throat, redness, pain when swallowing, and sometimes enlarged lymph nodes.
Nose deformities
A deviated septum and nasal polyps can cause breathing difficulties, chronic nasal congestion, and increased risk of sinus infections. Surgical procedures such as septoplasty or endoscopic polyp removal are often required to resolve these problems.
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears)
Tinnitus can range from mild irritation to severe hearing impairment. Causes vary, from noise exposure, infections, ear injuries, to vascular problems. An ENT specialist will conduct a thorough diagnosis and recommend appropriate treatment.
Sleep apnea
This disorder, characterized by temporary cessation of breathing during sleep, is often associated with airway obstructions due to enlarged tonsils, nasal problems, or soft palate issues. Treatment may involve surgery or the use of CPAP devices.

Why choose the PULS team of otorhinolaryngologists?
- Expertise comes first – Our team is led by Dr. Nevena Stošić, an otorhinolaryngology specialist with many years of experience in diagnosing and treating ENT conditions. You are in the hands of true experts.
- Comprehensive diagnostics in one place – In addition to ENT examinations, you can also undergo X-rays, pulmonary specialist consultations, and laboratory analyses at our facility. This allows for quick and precise access to all necessary information.
- Accessibility and fast service – Without the need for multiple trips to different locations, everything you need for quality diagnostics is available in one place. Our goal is your comfort and quick problem resolution.
- Modern technology – Puls uses the latest medical equipment, ensuring accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
What does an ENT specialist examination look like?
An examination by an ENT specialist includes a detailed inspection of the nasal cavity, throat, and ears using specialized instruments. The doctor will ask questions about symptoms, the duration of the problem, and any previous treatments. Depending on the symptoms, additional tests such as audiometry or endoscopy may also be used.
Preparation for an ENT examination
Before the ENT examination, it is important to bring all relevant medical documents, including the results of previous tests and treatments. Avoid using ear-cleaning products before the examination so the specialist can more accurately assess the condition.
Common diagnostic methods during ENT examinations
ENT examinations often include the following diagnostic methods:
- Tympanometry to assess middle ear function.
- Audiometry for hearing tests to detect hearing loss and determine its degree.
- Vestibulometry to assess the function of the nerve responsible for hearing and balance.
- Microscopic ear examination allows for the precise detection of pathological changes on the eardrum.
- Swabs from the throat, ear, nose, and tongue to detect the presence of bacteria and other infection-causing agents.
- Otoread or OAE hearing test for newborns to detect hearing impairment early.
- BERA neurological test to assess auditory function in the brainstem for adults.
These methods allow otorhinolaryngologists to quickly and accurately diagnose and begin appropriate treatment.
You can check the prices of ENT examinations and diagnostic procedures in our price list.
