Home » Services » Ultrasound (Ultrasound Diagnostics) » Doppler of the Hands Blood Vessels
Doppler of the Hands Blood Vessels (Upper Extremities)
What is the color doppler of blood vessels of the upper extremities?
Color Doppler of blood vessels of the upper extremities is a non-invasive diagnostic method that combines conventional ultrasound with color Doppler technology to visualize blood flow in the arteries and veins of the upper extremities (arms and hands). This method allows doctors to assess blood circulation, identify potential problem areas in blood vessels and diagnose vascular problems.
Color Doppler of upper extremity blood vessels is a quick, painless and safe procedure that is often used to assess vascular health and diagnose problems with blood flow in the arms and hands. This test can be very helpful in making an accurate diagnosis and planning appropriate treatment if any vascular problems are detected.
When is the color doppler of the upper extremities best method to use?
- If there are certain symptoms or signs that indicate possible vascular problems or disorders in that area: pain in the arms or hands, a feeling of pain, tingling or numbness in the hands, if your hands turn blue or pale white, swelling of the hands or hands, cold hands, slow-healing wounds, weak pulse in the hands, swollen or enlarged veins
- Diagnostics of peripheral arterial diseases: with people that have symptoms such as pain in the arms during activity (intermittent claudication), color doppler can help evaluate the blood flow in the arteries of the arms and detect possible narrowings or blockages.
- Venous insufficiency: Color Doppler is used to determine the presence and degree of venous insufficiency, which can cause swelling of the hands, varicose veins, or skin discoloration.
- Monitoring of vascular surgery: After upper extremity arterial or venous surgery, color Doppler can be used to monitor the functioning of vascular grafts and assess blood flow through the operated areas.
- Thrombosis risk evaluation: Color Doppler can help assess the risk of blood clots (thrombosis) in the veins of the upper extremities, especially in people with risk factors such as prolonged immobilization, pregnancy, or use of oral contraceptives.
- Evaluation of arteriovenous fistulas: People undergoing hemodialysis for kidney failure may have arteriovenous fistulas (direct connection between arteries and veins for easier access during dialysis). Color Doppler is used to monitor blood flow through these fistulas.
- After a hand injury, especially if there is a suspicion of vascular problems caused by the injury: control of circulation, assessment of arterial damage, detection of thrombosis, assessment of venous insufficiency
- Malignant processes in the breast: Color Doppler can reveal increased vascularization in the area of the tumor, which may indicate the presence of a malignant process. This can complement other diagnostic methods, such as mammography, breast ultrasound, and biopsy, in order to make an accurate diagnosis and plan appropriate treatment. monitoring the reaction to therapy and observing possible complications. It is important to note that color doppler hand is not a standard procedure for diagnosing malignant processes in the breast or monitoring after radiation. The decision to apply this procedure depends on the physician’s clinical judgment and specific circumstances
- Coarticulation of the aorta; Hand color Doppler can be a useful diagnostic procedure to assess blood circulation in patients with coarctation of the aorta. This procedure enables the visualization of blood flow in the arteries of the arms and hands in order to detect possible changes in circulation caused by the narrowing of the aorta.
How long does the color doppler examination of the upper extremities take?
How to prepare for color doppler of the upper extremities?
- Tell your doctor about your medications: Before your appointment, tell your doctor about all the medications you are taking, including prescription and over-the-counter medications. Some types of drugs, especially those that affect circulation, can affect the results of the examination.
- Clothing and jewelry: On the day of the exam, dress comfortably and be sure to wear clothing that allows you to easily expose your arms, as the technician will need to access your upper extremities. Also, avoid wearing jewelry or restrictive items on your hands to allow for better placement of the ultrasound transducer.
- Diet and fluids: Normally, there are no specific dietary or fluid requirements before this examination. You can eat and drink normally before the examination.
- • Previous results and reports: If you have already had previous medical examinations or tests related to the upper extremities, bring the previous results and reports with you for the doctor to review.
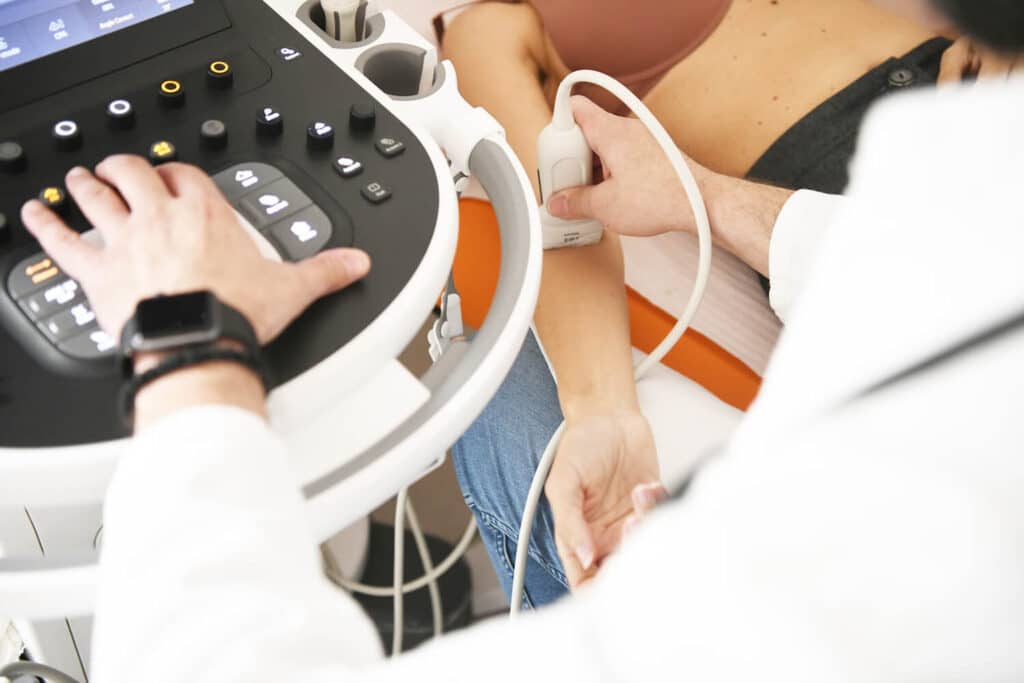
What happens during a color doppler examination of the upper extremities?
- Patient preparation: The patient will be placed on the examination table, and the arm or hand to be examined will be placed in an appropriate position to allow access to the blood vessels.
- Application of the gel: The gel is applied to the skin in the place where the examination will be performed. The gel improves the transmission of ultrasound waves and facilitates the placement of the transducer.
- 3. Placement of the transducer: An ultrasound transducer is a device that emits and receives ultrasound waves. A technician or doctor will place a transducer on the skin over the area where the arteries and veins to be examined are located
- Imaging of blood flow: When the transducer is placed in the right place, the ultrasound will be emitted towards the blood vessels. The reflected ultrasound waves are returned and used to produce real-time images of blood flow.
- Color doppler display: Instead of a standard black and white ultrasound image, color doppler allows the display of blood flow in different colors. For example, blood moving toward the transducer may be displayed in red, while blood moving away from the transducer may be displayed in blue. This allows easier visualization and understanding of blood flow in blood vessels.
- Imaging and measurement: The technician will take pictures and measure the speed of blood flow in different parts of the arteries and veins.
- Completion of the examination: When the examination is complete, the technician will review the obtained images and results. The results will be forwarded to the doctor who will interpret and make a diagnosis.
What problem or condition can Doppler blood vessels of the upper extremities show?
Peripheral arterial disease
Venous insufficiency
Thrombosis
Raynaud’s syndrome
Aneurysm
Vasculitis
Presence of vascular masses or tumors
After surgical procedures
Vascular disorders
Who assesses the results of the upper extremity color doppler test?
What additional tests can the doctor recommend based on the color doppler results of the upper extremities?
- Angiography: This is an invasive procedure in which a contrast agent is injected into the blood vessels of the arms, and then X-rays are taken to obtain a detailed visualization of the arteries and veins.
- Pressure Doppler: This test uses ultrasound to measure blood pressure at different points in the arms, which helps assess the degree of narrowing or blockages in the arteries.
- CT angiography: Computed tomography (CT) angiography uses X-rays to create detailed images of the blood vessels in the arms with the help of intravenous contrast.
- MRI Angiography: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) angiography uses a magnetic field and radio waves to create images of blood vessels. This test may also use a contrast agent for better visualization.
- Blood coagulation tests: If thrombosis is suspected, the doctor may recommend blood coagulation tests to check the risk of blood clots.
- Tests for autoimmune diseases: If vasculitis or other autoimmune diseases that can affect the blood vessels are suspected, the doctor may recommend tests for autoantibodies or other markers of inflammation.
- Vascular provocation: In some cases, the doctor may recommend vascular provocation testing to assess how the arteries respond to certain stimuli (for example, cold).
