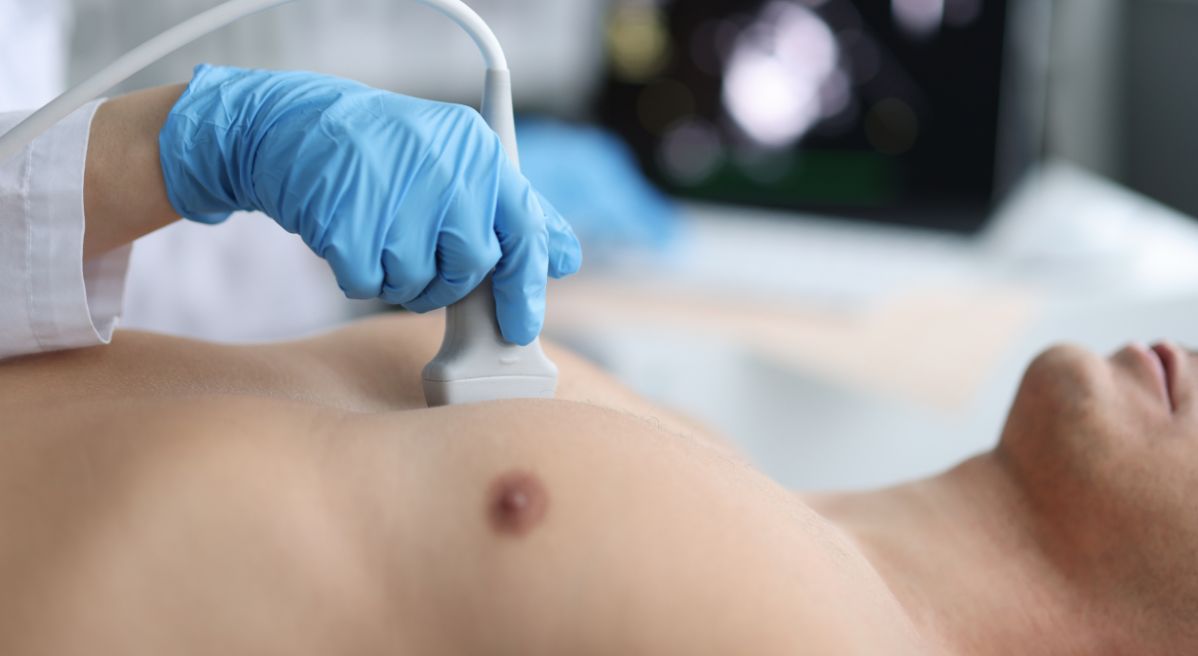
In some patients, the expert will see the existence of a heart problem at a glance, but in those situations, it is most likely that the development of the disease has already progressed. Early diagnosis is crucial for the successful treatment of cardiovascular diseases, but it will often happen that the patient does not feel any problems in the early phase of the disease.
A complete heart evaluation is a set of tests that is recommended not only to people with severe symptoms, but also to all those who have predispositions of any kind for the development of these diseases, as well as to all those who take care of the condition of their organism.
What tests does a complete heart evaluation involve?
The complete heart evaluation is designed to include the necessary tests that can give doctors important information about the condition of your cardiovascular system and it includes:
● Cardiovascular risk assessment
● Complete blood analysis test
● Ultrasound of the heart
Cardiovascular risk assessment
Determining the risk that a patient has for the development of cardiovascular diseases (CVD) as accurately as possible is extremely important for prevention, but also for avoiding worsening of the condition and fatal outcome.
Doctors will use the SCORE chart to define risk:
● Very high cardiovascular risk: SCORE 10% and higher – will be characteristic of patients who have already registered a cardiovascular disease, diabetes with another or more risk of cardiovascular disease or a serious kidney disease.
● High cardiovascular risk: SCORE 5% -10% – characteristic of patients with familial dyslipidemia and severe hypertension, diabetes, organ damage and moderate kidney issues
● Moderate cardiovascular risk: SCORE 1% -5% – most middle-aged people will belong to this group
● Low cardiovascular risk: SCORE below 1%
Cardiovascular risk does not depend only on the diseases that a person has or does not have, on genetic predispositions, but also on the way of life, so obesity and smoking will certainly affect its increase. If you belong to the group with moderate risk, changing habits and lifestyle should be enough to prevent the development of these types of diseases.
Diabetes is mentioned as a disease that increases the chances of developing CVD in as many as two categories. There are reasons for that. People who have diabetes, especially type 2 diabetes, often have high blood pressure, high cholesterol and triglycerides, and if they are also characterized by obesity and lack of physical activity, the risk increases even more.
Cardiovascular risk tests for: diabetes, cholesterol, obesity and hypertension are performed in our institution.
Complete blood test
The blood test also gives the doctor important information about the condition of your cardiovascular system. What we would single out as especially important are: complete blood count with leukocytes, CRP, sedimentation, glycemia, urea, creatinine, cholesterol, AST, ALT, GGT, sodium, potassium. Depending on the purpose of the examination and each patient, the list may be different.
What is an ECG?
An electrocardiogram (ECG) is a graphical record of the electrical activity of the heart.
Electrocardiography is a painless, safe method and does not last long, only a few minutes. The patient should lie still, not move in order for the result to be valid. Up to twelve electrodes are placed on his chest and limbs and they record how his heart beats. The computer will record the information and display it on a monitor or paper in the form of waves.
The ECG of the heart consists of waves marked with the letters P, R, S, T. The wave P detects the reaction of the atria of the heart at the beginning of the pulse, R and S detect the reaction of the ventricles to the pulse, and T is the reaction of the ventricles at the end of contraction. There are intervals between the waves. Based on the wave shape and the length of the interval, it is possible to notice disorders in the work of the heart.
The doctor can refer you to an ECG examination if you have any issues, before the operation when anesthesia will be used, due to some genetic predispositions, if you are dealing with a stressful occupation, but also preventively as part of the annual examination.
An ECG scan can detect:
● Arrhythmias
● If you have had a heart attack
● Whether the heart valves are functioning well
● If you have dilation and thickening of the atria and ventricles
● Whether pacemaker works well, for instance
No preparations are needed for the ECG examination (only if you have therapy, consult a doctor whether to take it), and after that the patient can continue with regular activities.
When the electrocardiography is done, you get the results immediately. The doctors from our team will explain their meaning in detail and give further guidelines.
What is an ultrasound or echo of the heart?
In addition to the ECG, echocardiography or “echo” heart test is also one of the most commonly used methods for detecting heart problems. It is completely safe and painless, there are no restrictions in terms of the patient’s age, and it can be performed at any age.
Ultrasound can provide information about the size and shape of the heart, the place of tissue damage, the appearance of the heart valves, with the help of which it is possible to detect congenital heart anomalies.
This type of testing is definitely recommended for people with pronounced symptoms of heart disease, but it is desirable to do it even when the patient does not feel any issues as part of preventive examinations. Sometimes it is done before operations, in oncology patients or to monitor the effects of therapy.
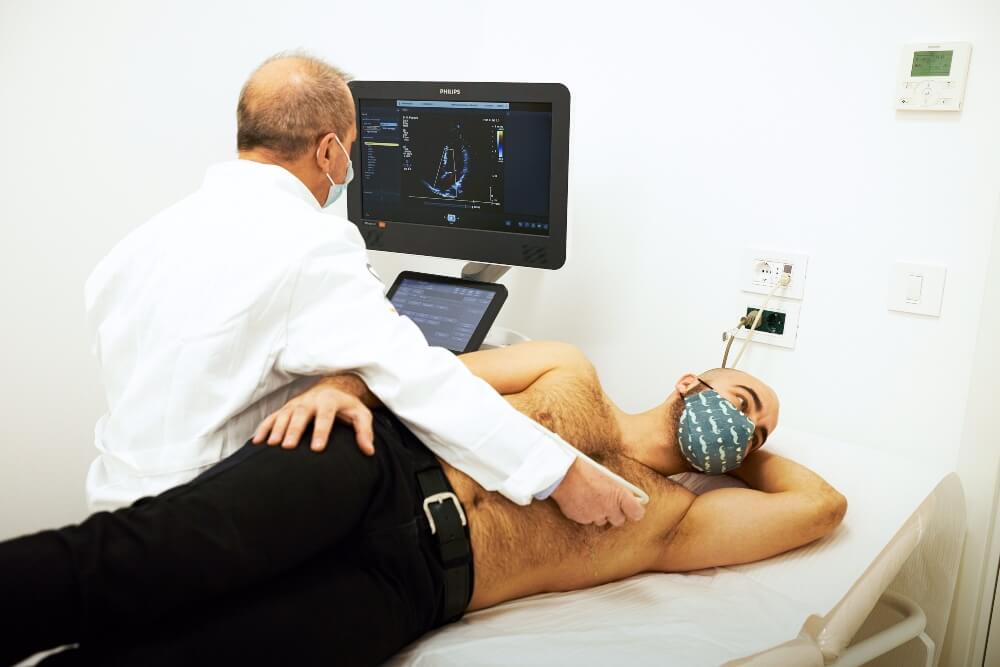
There are several types of echocardiography:
● Transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) – this is a standard ultrasound of the heart, the probe is placed on the anterior thoracic wall of the patient, through which ultrasound waves pass and thus an image is obtained. If, for example, the ribs block and prevent the heart from being seen well, the patient is given contrast to make the picture clearer. Contrast is safe.
● Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) – this method is invasive and is performed with the help of a special probe that is inserted into the patient’s esophagus, and then gives images directly behind the heart. The quality of this recording is at an even higher level, it is clearer. If it is not possible to perform a standard ultrasound of the heart, then this one is done, which is uncomfortable and the patient therefore received local anesthesia.
● Doppler echocardiogram – is a non-invasive method that gives a more complete picture of the heart and blood vessels. In this way, the doctor can monitor and measure the speed and direction of blood flow in the heart.
● Stress echocardiogram – involves imaging the heart wall. First, the resting heart is recorded, and the direction of movement of the heart wall is determined. Then the patient should do some exercises or walk on the treadmill, in order to move his body from a state of rest. After that, recordings of his heart are made “under stress” in order to see the movement of the heart wall at the peak of the heart work.
● Three-dimensional echocardiography – is a modern method and enables real-time imaging in three dimensions, so it is possible to make an even better assessment of cardiac pathology.
The standard ECHO of the heart is usually done, it is performed in the office, the patient is lying on the table, and it is necessary to take off his clothes to the waist. The doctor applies the gel and spreads it across the chest with a probe. He may ask the patient to breathe in a certain way or to turn to the left side.
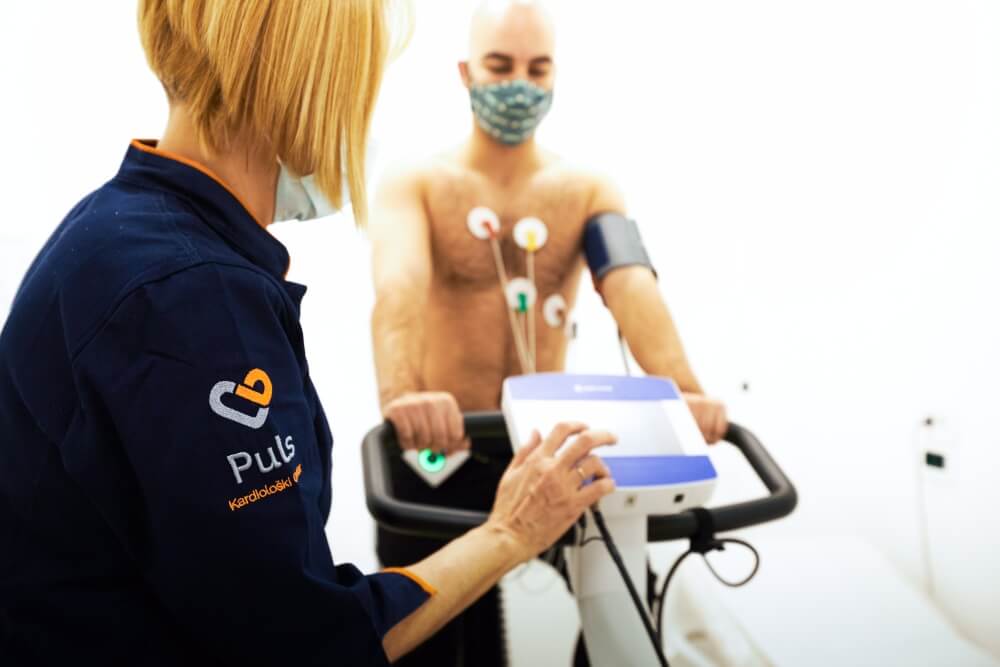
What is ergometry?
Ergometry is a non-invasive method that involves exposing the patient to physical load and monitoring the impact of the load on the function of the heart. The patient walks on the treadmill walking belt or uses an ergocycle while the load increases every few minutes. Electric heart activity, blood pressure, heart rate per minute are measured all the time, and respiration is monitored.
The ergo test is performed to assess the condition of the blood vessels, to detect arrhythmias or to monitor the success of prescribed therapy and treatment of heart problems.
What is coronary angiography and is it included in the total examination of the heart?
Coronary angiography is an invasive method and is an examination of the coronary arteries using a catheter and a contrast agent. It involves inserting a catheter through a small incision in the groin, arm or neck. The procedure takes about half an hour and provides important information about the condition of blood vessels.
If during the procedure, narrowing of the blood vessel is noticed, which threatens to endanger the patency of blood through that blood vessel, the patient is fitted with a stent. The stent serves to strengthen the blood vessel and to widen the narrowing, in order to restore patency.
This method is not included in the basic analyzes performed as part of a total heart examination. If you need coronary angiography, the price can also be an important piece of information. We are here to answer all your questions.
How do I know if I need a complete heart evaluation?
If you have any problems that indicate cardiovascular problems or you belong to the risk group, a complete heart evaluation is necessary for you, so that doctors can identify the problem as soon as possible, define the problem and recommend therapy and further steps in treatment.
It is even better not to wait for the appearance of problems, but to preventively approach this detailed test, which includes the most valid methods for detecting cardiovascular problems. Early diagnosis and timely treatment give the best results. Don’t wait to feel the pain in the area of the heart, think about your heart in time.
You can perform all the above analyzes in one place, in the Pulse Cardiology Center, where highly qualified experts and the most modern equipment are waiting for you, and you will receive the results on the same day. Examinations are scheduled within 24 hours and performed within 48 hours. Call us, we are waiting for you.