CT angiography is one reliable method for diagnosing this vascular problem, making detection relatively straightforward. However, what complicates detection is the fact that patients often remain unaware of any vascular changes for a long time and may not seek medical attention until later stages. As with many diseases, symptoms are frequently absent, making regular preventive check-ups crucial for early detection before any specific signs or emergency situations arise. If you have an aneurysm or know someone with this condition, it is important to learn as much as possible about the nature of the disease, its diagnosis, treatment options, and strategies to prevent fatal outcomes.
What is an aneurysm?
An aneurysm is a localized dilation or bulge in blood vessels that occurs due to the weakening of certain parts of the vessel wall. There are various reasons why this can happen; it can be a hereditary condition, or it can be caused by other diseases or lifestyle factors.
Depending on where the aneurysm is located, it can be:
- Cerebral aneurysm
- Aortic aneurysm (abdominal and thoracic)
Cerebral (brain) aneurysm
A cerebral aneurysm is a sac or bulge that forms on a blood vessel in the brain, resembling a small pouch or spindle. Initially, these bulges are small, but they can grow over time. Aneurysms are dangerous because they have the potential to rupture, leading to bleeding in the affected area.
Depending on the severity of the bleeding, the consequences can include nausea, loss of consciousness, coma, and even death. In the base of the brain, there is a network of arteries that further branch out into smaller arteries responsible for supplying blood to the brain. It is at these branching points that cerebral aneurysms commonly develop.
Symptoms of a cerebral aneurysm
Symptoms often occur when the aneurysm is already in a critical condition or has ruptured. Patients may experience the following symptoms before an aneurysm rupture:
- Nausea
- Intense headaches
- Double vision
- Drooping eyelid
- Pain behind the eye
- Unequal pupil size
After an aneurysm rupture, the following signs may appear:
The most severe headache the patient has ever experienced
- Nausea and a strong urge to vomit
- Stiffness in the neck
- Loss of consciousness
- Coma
Very often, a ruptured aneurysm leads to a fatal outcome, which is why this condition is extremely dangerous!
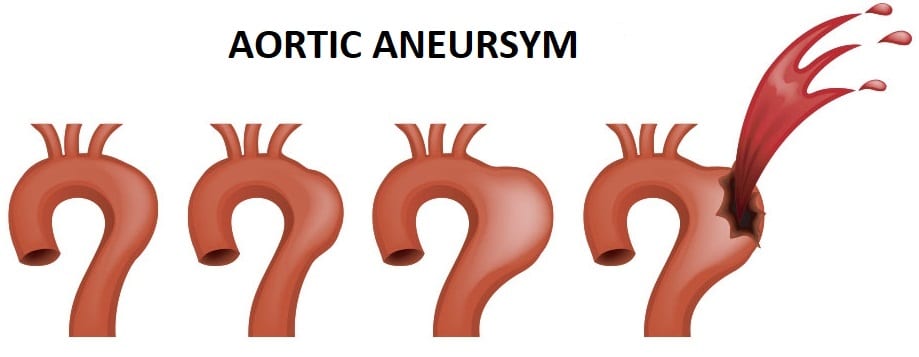
Aneurysm of the aorta
An aortic aneurysm is a dilation in a weakened part of the aorta. The aorta is the largest artery responsible for carrying blood from the left side of the heart to all parts of the body.
Depending on the location of the problem in the aorta, there are two types: thoracic aneurysm and abdominal aneurysm.
Thoracic Aneurysm
When the dilation and weakening of the blood vessel occur in the thoracic (chest) portion of the aorta, it is called a thoracic aneurysm. Similar to cerebral aneurysms, it is crucial to detect it early to avoid more severe consequences. If left undiagnosed and untreated, it can eventually lead to a rupture of the aorta, resulting in significant bleeding, despite the aorta being a large blood vessel.
Abdominal Aneurysm
The abdominal aorta, similar to the thoracic aorta, can develop a dilation on its wall known as an aneurysm. This type of aneurysm is equally dangerous as the previous ones and, like them, often develops over the course of years without showing symptoms until it ruptures.
When a rupture of an abdominal aneurysm occurs, immediate intervention is necessary to save the patient’s life. Under normal circumstances, the diameter of the distal part of the abdominal aorta is around 2 cm, but due to the development of an aneurysm, it can increase to over 6 cm before it ruptures. Because of the prolonged nature of the process, patients usually have time to detect the disease, making preventive examinations crucial. Your body won’t tell you that something is wrong in the early stages of the disease, but changes can be detected during a medical examination.
If you wish to schedule a cardiac examination in Belgrade, our clinic is the right place for you. You won’t have to wait in line, and all services can be provided on the same day.
Symptoms of Aortic Aneurysm
Symptoms of Thoracic Aneurysm
Symptoms of thoracic aortic aneurysm often resemble symptoms of other heart and cardiovascular diseases:
- Upper back, neck, shoulder, and jaw pain
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath and cough
- Hoarse voice
- Swallowing difficulties
Signs indicating a ruptured thoracic aneurysm:
- Sudden and persistent sharp chest pain
- Pain that radiates to the back
- Drop in blood pressure
- Difficulty breathing
- Loss of consciousness
Symptoms of Abdominal Aneurysm
During the period when the aneurysm is small, patients may not even suspect its presence because they feel normal and have no difficulties. When signs indicating its presence start to manifest, they usually include:
- Pulsating abdominal pain
- Pulsating lower back pain
Symptoms indicating a ruptured abdominal aneurysm:
- Persistent severe pain in the abdomen or back
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Low blood pressure and high pulse rate
- Breathing difficulties
- Loss of consciousness
How Aneurysms Develop
In essence, all aneurysms can develop in a similar way and for similar reasons, as they involve changes in the walls of blood vessels. Some individuals have genetic predispositions to develop aneurysms, so if you have a family member with this condition, it is important to inform your doctor and regularly monitor your blood vessels. People with Marfan syndrome (an inherited disorder that affects connective tissues) are always at high risk.
Aneurysms can also occur due to aortic injury or congenital anomalies in the aortic wall. On the other hand, certain diseases and habits can act as triggers for their development, including atherosclerosis, high blood pressure, and smoking.
Age is also a significant factor. Just as the number of individuals affected by cardiovascular diseases increases in older populations, the same applies to this problem. Aging is a process that inevitably affects blood vessels to some extent. By living a healthy lifestyle and adopting healthy habits, we can somewhat mitigate the aging process of our blood vessels and, consequently, reduce the likelihood of developing related issues solely due to age.
Diagnosing an Aneurysm
The diagnosis of any type of aneurysm is not particularly complicated. As we have already emphasized, the most important step is to actually undergo regular check-ups before the onset of any symptoms. To accomplish this step, we must be aware of the existence of numerous diseases that can persist without showing any signals that something is wrong.
When a doctor suspects the presence of an aneurysm, they may recommend one of the following methods:
- Chest X-ray
- CT angiography
- CT scan of the heart and lungs
- MRI of the chest and abdomen
Aneurysm treatment
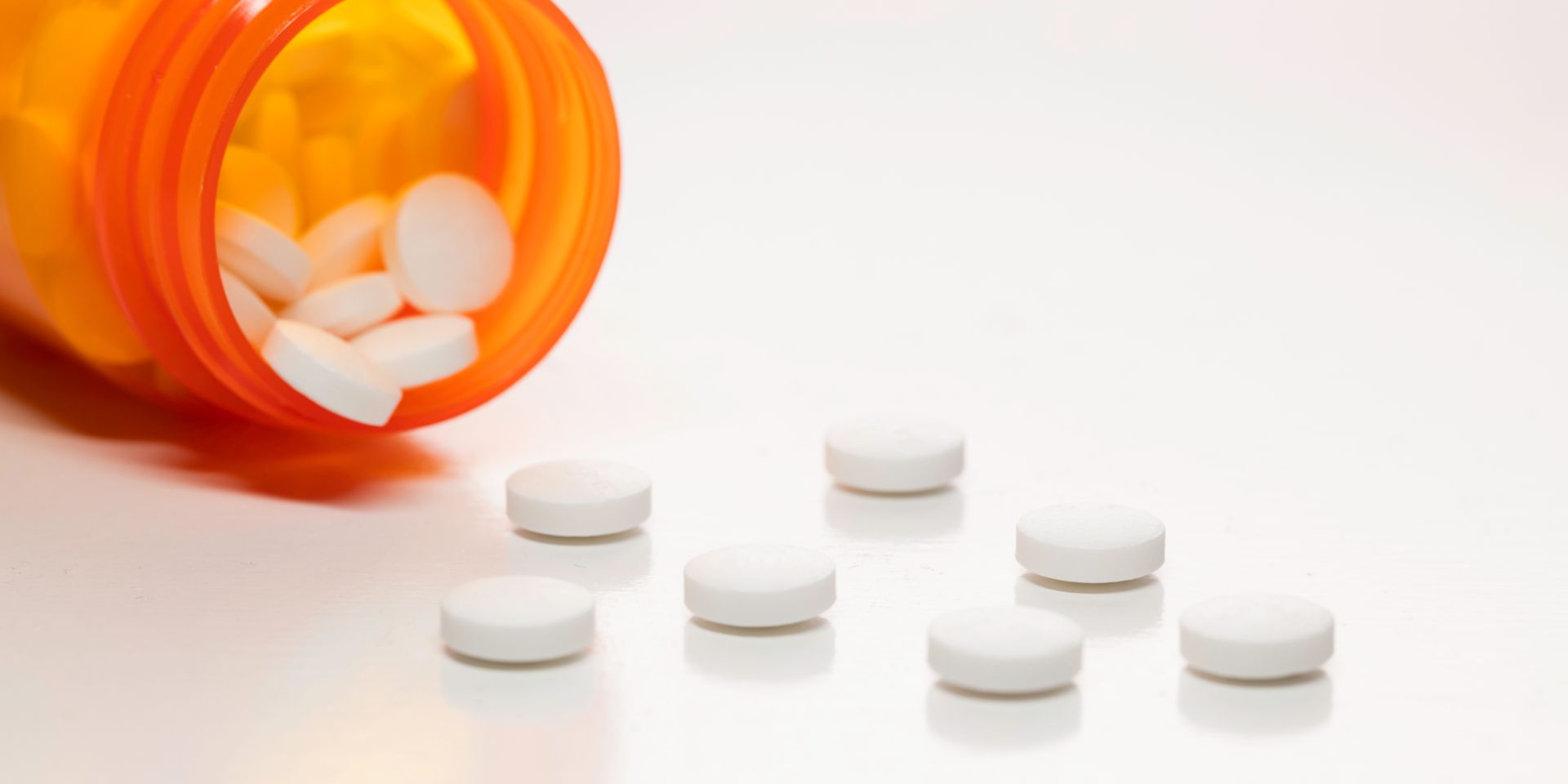
Treatment of an aneurysm can be approached in several ways. When it is detected in the early stage, regular monitoring and imaging once or twice a year are usually advised. Medications may be prescribed at some point, commonly beta-blockers, ACE inhibitors, statins, but these medications cannot make the aneurysm disappear. Surgery can also be an option, but it is recommended when the condition is more dangerous and severe, such as when the aneurysm is larger or in cases where the patient’s condition poses an increased risk of rupture.
Aortic aneurysms can be treated by endovascular placement of a stent or by open surgery involving the abdominal or thoracic part of the aortic wall (depending on the location of the problem) and the placement of a graft. The latter procedure is more serious, and the recovery after it is more challenging compared to stent placement.
When a patient experiences severe and continuous pain in the chest, abdomen, or head, their first reaction should be to seek emergency medical help. There is always a chance of surviving an aneurysm rupture, but the risk associated with this condition is enormous. Do not wait for symptoms and pain, undergo preventive screening at the Pulse Cardiology Center, and stay one step ahead! Take control of your health.