The pediatrician who follows the child from birth and the parents play a key role in recognizing the need for further analysis. There are certain symptoms that will indicate the possibility of a heart disease and they will very often manifest themselves already in the first few weeks of a newborn’s life.
Of course, this is not always the case, and if it happens that the pediatrician notices that your child needs a cardiology examination when he is a few years old, you should do it right away. The fact that a child lives for years with a problem that was not immediately detected does not mean that the problem is completely harmless.
Symptoms of heart problems in children
Symptoms can be different, stronger or less pronounced, and sometimes they will not appear for years, but when they do appear, they should be taken seriously.
In newborns, heart problems are often noticed immediately because they can be obvious:
- the baby gets tired quickly while eating
- sweats profusely in the head area while eating
- does not gain weight
- is lethargic or irritable
- breathing irregularly
- urinates less often
In older children, symptoms such as:
- chest pain
- tiring
- constriction in the heart region
Chest pain in children
Chest pain in children is not a common symptom of heart disease, but it can be. Research has shown that in only 5% of cases, chest pain in children is eventually connected to some problem such as heart tissue or muscle inflammation or frequent tachycardia (rapid heartbeat). What is specific about the pain that indicates these problems is that it is very strong, that it also affects proper breathing, so the child will have difficulty breathing and will be in a bad general condition, and in addition to all this, a high body temperature may occur.
If your child complains of pain of this type, he should be examined by an expert, a pediatric cardiologist, in order to determine the cause.
Regardless of whether the pain is the result of an inflammatory process or a congenital problem, without the right diagnosis, the treatment cannot be successful. The Pulse cardiology center is also suitable for the youngest who need cardiology diagnostic and treatment.

Heart murmur in children
A heart murmur represents the turbulent passage of blood through the heart. A heart murmur in children is a very common phenomenon, but in a huge percentage it is a physiological, that is, a harmless murmur that does not require treatment.
Such a noise can be noticed by a pediatrician, that is, heard using a stethoscope sometimes, and most often when the patient comes in due to an infection and the like. Its intensity quickly weakens, so during repeated or control examinations it is not heard, and after puberty it finally disappears.
Physiological noise disappears until puberty because then the body and muscles develop rapidly and the heart is located further from the stethoscope, so it is impossible to hear such quiet noises anymore. Apart from that, they are not accompanied by any other symptoms.
On the other hand, organic noise requires further analysis and treatment. This type of noise will not lose its intensity, it can even get stronger, and pediatricians have no problem recognizing noises that require additional examination.
When a pediatrician notices a heart murmur in children, if he suspects that it is organic, he will recommend further tests.
The pediatric cardiologist will first listen to the heartbeat with a stethoscope, after which he may recommend an echo of the heart (echocardiography, i.e. ultrasound of the heart), and possibly some other diagnostic methods depending on the situation.
ECHO of the heart – an ultrasound of the heart can provide information about the structure of the heart, the performance of the atria and ventricles, it can be seen how blood passes through the heart, whether there is a murmur, whether there is fluid around the heart, and the like.
It is important to know that ultrasound is a safe, secure and painless diagnostic method that can be used on any patient, regardless of age. It is completely safe for children to undergo an ultrasound. You get the results immediately after recording. At Pulse Cardiology Center, this diagnostic method is available to you without waiting.
Irregular heartbeat – arrhythmia
Arrhythmia implies an irregular heartbeat that can be accelerated (tachycardia) or slowed down (bradycardia). This type of problem occurs in children as well as in adults and may be the result of some congenital heart defect, metabolic disorders, hormonal changes, changes in electrolyte levels, etc.
Arrhythmia, like the murmur, can be transient and harmless, but the assessment should be made by a pediatric cardiologist.
Some arrhythmias will require long-term treatment or intervention, but it is crucial to detect them and treat them in time so that they do not affect the general condition of the child and his development.
An examination by a specialist may include:
- anamnesis – taking data about the patient, his complaints, when problems occur, how long they last, etc.
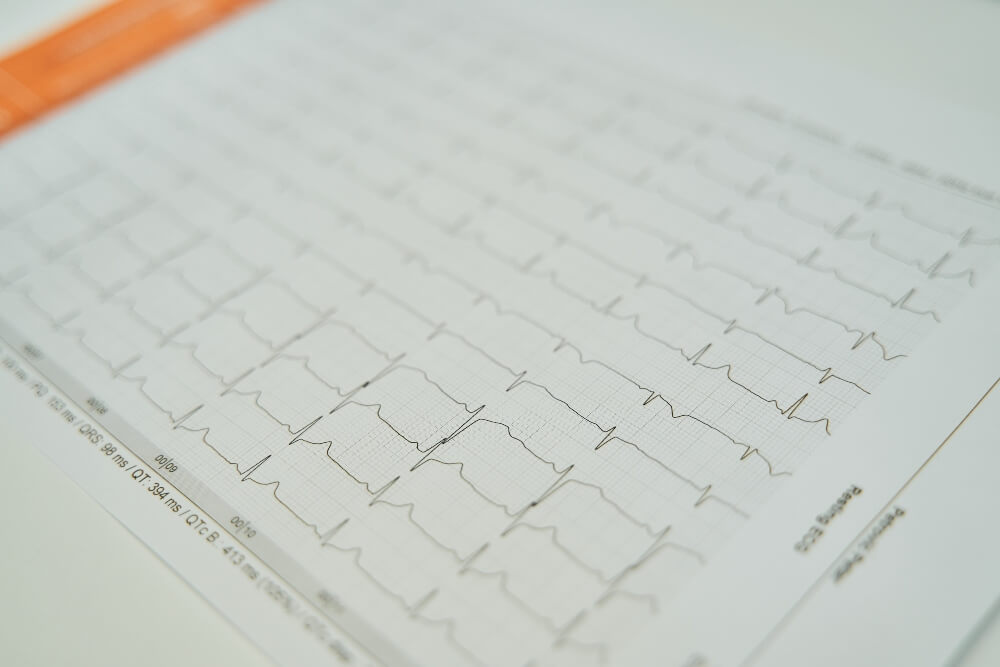
- ECG, i.e. electrocardiogram – involves measuring and recording the electrical activity of the heart.
- 24-hour holter – represents the measurement of the electrical activity of the heart during 24 hours. While wearing a holter, the patient performs daily activities in order to monitor the heartbeat in certain situations during the day.
Congenital heart defects
Congenital heart defects are also not rare, but not all of them are life-threatening. Some do not carry any symptoms and do not require treatment, many can be treated or surgically resolved, after which the patient will lead a normal life without any consequences.
However, a small percentage of birth defects will require long-term treatment, possibly multiple interventions, after which the child will still have to be watched and will not be able to perform all activities in the future. Such defects are the most difficult, but also the rarest.
The reasons for the appearance of these problems are usually a hereditary factor or some error in the genetic material. In addition, maternal infections during pregnancy, exposure to harmful substances, or maternal diabetes during pregnancy can also increase the chance that the newborn will have a heart defect.
As with all heart diseases, quick and accurate diagnosis is crucial and very often after the birth of a child, more serious problems are noticed immediately or during the first weeks of life.
Sometimes it is possible to spot a problem already during pregnancy as part of a regular ultrasound that includes fetal echocardiography (examination performed between the 20th and 25th week of pregnancy), because the baby’s heart is examined in detail and the number of blood vessels and blood flow are checked. Of course, this diagnostic method has limitations, like everything else, and it is possible that the anomaly will not be noticed even then.
A diagnostic method that can detect anomalies on the heart and blood vessels with great reliability is echo of the heart, i.e. ultrasound of the heart. When the baby’s development is complete and it is born, then the doctor will have a clearer view with an ultrasound.
We repeat once again that ultrasound imaging does not harm the baby and provides extremely important information about the appearance and function of the heart.
How cardiological examination is performed
A pediatric cardiologist specializes in working with children up to 18 years of age. His approach is very important so that the child feels relaxed and safe during the examination.
The first thing they will do is take information about the child, the illness, the condition the child is in, when the symptoms appear, what the symptoms are, family illnesses, and that is why it is important that the parent is also present.
After that, depending on the situation, your child may be referred for tests such as:
- echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart)
- EKG (electrocardiogram)
- 24-hour holter monitoring, etc.
After detailed examinations, the diagnosis and recommended method of treatment will be defined.
Visiting the doctor in childhood can be stressful because children are not used to such situations. That is why it is important to choose a place where both you and the child will feel safe and important. For us, every patient comes first, because we are here for you.