Early diagnosis and fast treatment are perhaps the most important factors that can prevent fatal consequences.
Pulse Cardiology Center has a modern Cath Lab in which we can make a fast diagnosis and emergency or elective procedures.
What Is Cath Lab?
Cath Lab is a specially equipped room in which minimally invasive procedures – interventional procedures are performed in order to diagnose and treat patients with cardiovascular problems, patients who have problems with circulation in the legs, and people who have survived a stroke.
At the Pulse Cardiology Center, you can perform all important procedures in a vascular room that is surgically sterile, modernly equipped, and connected to a recovery room.
In addition to being equipped to the highest standards and having the best professionals trained to work in this room, we can boast with another very important factor and that is its availability.
You will receive an appointment for an examination or intervention as soon as possible, which is crucial for your life and health. With us, you don’t have to wait, all the interventions that are performed in it are scheduled quickly and end within one hospital day.
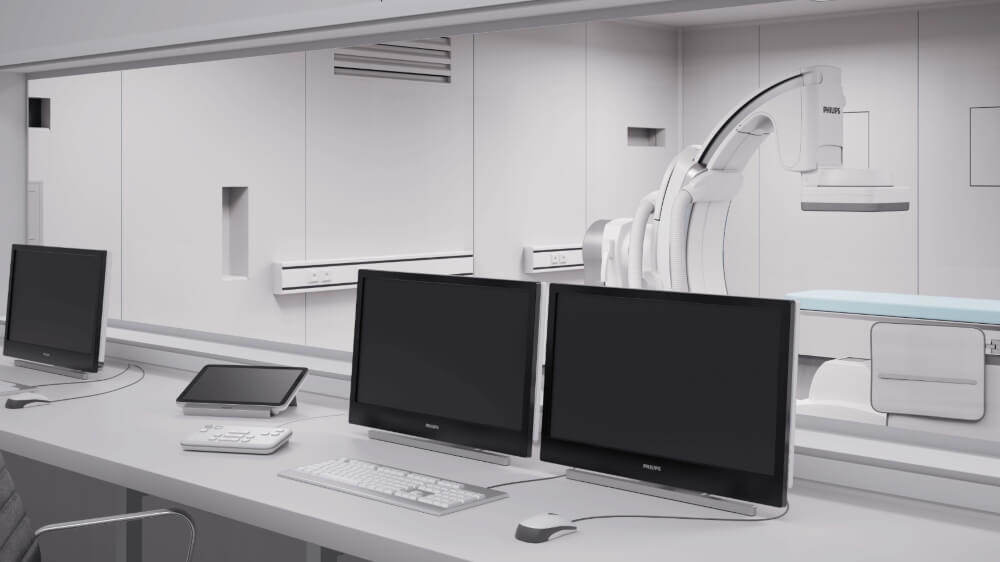

What Procedures Can Be Performed in the Cath Lab?
Cath Lab is necessary for many diagnostic and therapeutic procedures such as:
- Coronary angiography – an invasive procedure that uses a special dye (contrast material) and x-rays to see how blood flows through the arteries in your heart.
- Angiography of peripheral and visceral arteries – visualization of peripheral and visceral arteries using contrast material and x-rays
- Stent placement – stent is a tiny, expandable metal mesh coil that is put in a narrow coronary artery. Stent prevents the artery from narrowing or closing again, so that blood can flow through the blood vessel undisturbed.
- Pacemaker implantation – pacemaker is a small electronic device, the size of a matchbox that is used for patients with slow heartbeats or irregular rhythm. The pacemaker sends electrical pulses to help the heartbeat at a normal rate and rhythm.
- Balloon angioplasty – a procedure in which a long thin tube called a catheter is used to open a narrowed coronary arteries. It is often used in combination with coronary stent placement.
- Pericardiocentesis – invasive procedure where fluid is aspirated from the sac that envelops the heart (pericardium). It is often performed in the setting of pericardial tamponade (buildup of fluid around the heart which prevents normal heart function) or for sampling fluid and sending it for furher diagnostic.
- Insertion of IVC filter in the inferior vena cava – an invasive procedure in which a thin flexible tube (catheter) is inserted into this vein. This procedure is important for patients with thrombosis of this vein.
- Sclerotherapy – a medical procedure used to eliminate varicose veins and spider veins.
- Cardiac electrophysiology procedures – a test performed to assess your heart’s electrical system or activity and is used to detect abnormal heartbeats or arrhythmia. It can also diagnose what caused the abnormal heart rhythm which is very important for treatment.
- Radiofrequency ablation (RFA) – a procedure in which a thin wire sends radiofrequency energy – heat to the areas of the heart which are responsible for abnormal rhythm. It is used for the treatment of some abnormal heart rhythms, like tachycardia.
- Cryoablation – one of the best treatments for atrial fibrillation in which a balloon catheter is used to locate and freeze the part of the heart that is responsible for an irregular heartbeat.
What Is Cardiac Catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization is an invasive diagnostic procedure for the detection and treatment of certain cardiovascular conditions.
During cardiac catheterization, a thin tube (catheter) is inserted into a blood vessel (usually artery) in the arm or groin area. On the video screen, the doctor can see the position of the catheter as it is threaded through the major blood vessels and to the heart. Through catheter contrast or other instruments can be inserted, depending on the diagnose and treatment plan.
For this procedure, a team of 4 medical staff is needed. If the patient has any discomfort during the intervention (the most common is feeling of heat in the head or body, which is the effect of the contrast being injected fast) they can communicate with medical staff, as the patient gets a local anesthetic.
The duration of the procedure is between 30min and 60min, sometimes a little bit longer. The radiation to which the patient is exposed during that period is totally acceptable.
Why Is the Cardiac Catheterization Done?
This procedure is done when ischemic heart disease is suspected when a patient has an acute coronary syndrome when a patient has unstable angina when a patient has some heart defects.
The following procedures can be done during cardiac catheterization:
- Cardiac ventriculography – contrast injection in heart chambers
- Coronary angiography – contrast injection in coronary arteries
- Angioplasty with or without coronary stent placement
- Transcatheter aortic valve replacement
- Pressure measurement in heart chambers
- Measurement of oxygen blood saturation on different levels of the heart using blood samples
- Pressure measurement after and before the narrowing in the coronary arteries
- Intravascular ultrasound (visualization of the inner layers of a blood vessel using ultrasound)
- Optical coherence tomography
- Myocardial biopsy
- Closing of the pathological openings between heart chambers

How Should You Prepare for Cardiac Catheterisation?
There are some important rules you should follow before this procedure.
8 hours before the intervention you shouldn’t eat and you can drink fluids up to 2 hours before the intervention. Also, you should not consume alcohol and cigarettes.
It is important to tell the cardiologist about all the medication that you take, so the doctor can tell you which medications are allowed before the procedure. For example, if the patient takes a drug called Metformin, he should stop taking it two days before the intervention, on the day of intervention, and two days after.
You should have someone to accompany you and to be with you up to 24h after the intervention because sometimes patients can have dizziness or collapse.
Side Effects of Cardiac Catheterisation
- Swelling at the side of catheter insertion
- Allergy to the contrast dye
- Damage to the artery where the catheter was inserted
- Infection (local or systemic)
- Arrhythmias
- Stroke, myocardial infarction, or death are very rare complications
What Is Arrhythmia?
Arrhythmia is one of the most common reasons for seeing a cardiologist. Term arrhythmia refers to a group of conditions that cause either irregular beating of the heart, fast beats, or slow beats. They can be followed by different symptoms, some milds some more serious, and sometimes the patient himself can feel the irregular beating of the heart.
Many different factors can affect the heart rhythm (stress, coffee, alcohol, excessive physical activity…) so the irregular heartbeat can be transient. Arrhythmias can be caused by heart problems (angina pectoris, myocardial infarction, congenital heart defects..) but also problems with other organs (thyroid, kidney, lungs..) can cause irregular heartbeat.
There are different types of arrhythmia:
- Bradycardia – slow heartbeat
- Tachycardia – fast heartbeat
- Irregular heartbeat, also known as a flutter or fibrillation
- Early heartbeat or a premature contraction
Arrhythmias can also be classified based on the origin in the heart:
- Upper chamber origin or supraventricular (sinus tachycardia, supraventricular extrasystole, supraventricular tachycardia, atrial tachycardia, atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter)
- Lower chamber origin or ventricular (ventricular extrasystole, ventricular tachycardia, ventricular fibrillation)
If your doctor suspects that you have irregular heart rhythm he will order an ECG or a Holter ECG, but sometimes electrophysiology which is done in the Cath Lab is necessary.
Belgrade is in the top cities in Serbia in terms of the numbers of CathLabs, and they exist in both private and state hospitals.
When choosing in which clinic should your procedure be done it is important to know that in our clinic the appointment can be made on the same day, which is very important for cardiovascular diseases since every postponement increases the risk of serious complications.
In Pulse Cardiologie Center the best experts in their fields, who are trained to handle the most modern equipment are waiting for you.