call us
Endovascular treatment for thoracic aorta
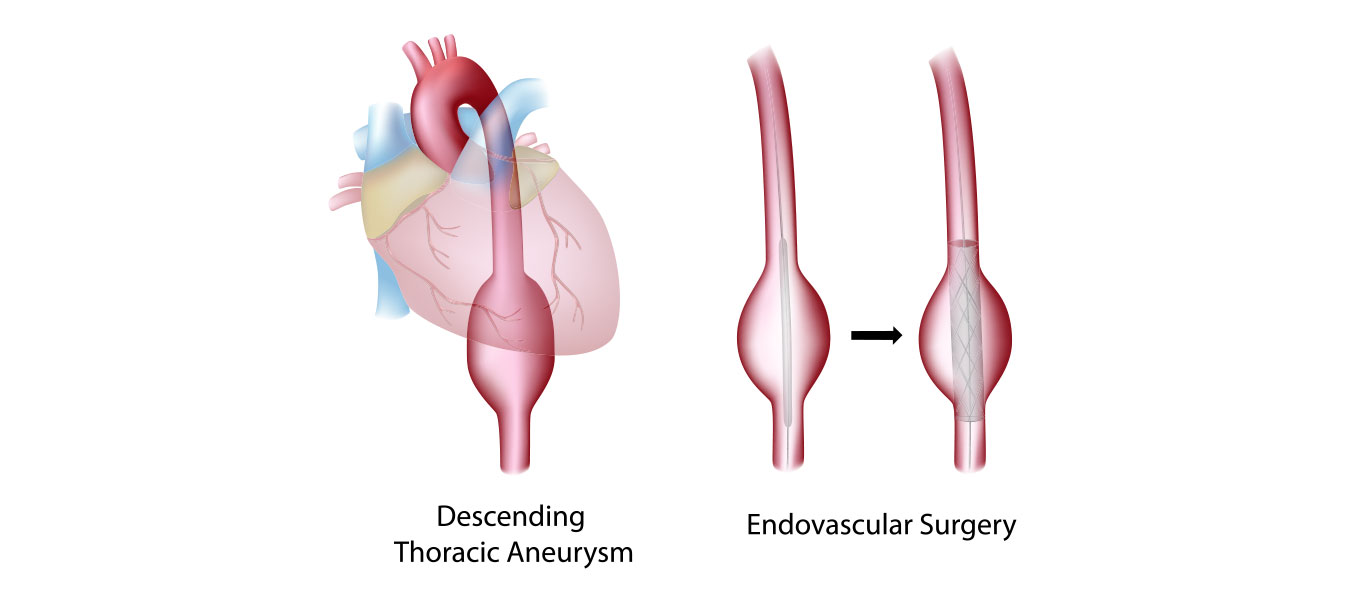
Thoracic aortic aneurysm – an abnormal bulge in the weakened aortic wall in the area of the chest, can cause various symptoms and often life-threatening complications. Due to the serious risks it poses, timely diagnosis and treatment of thoracic aneurysms are crucial.
The standard surgical treatment for thoracic aortic aneurysm is to repair an open chest aneurysm, but Pulse cardiologists are able to treat many thoracic and thoracoabdominal aneurysms (occur in the lower part of the thoracic aorta and the upper part of the abdominal aorta) with a minimally invasive procedure – endovascular stent graph.
This method replaces the previously unavoidable neurosurgical operation of blood vessel aneurysms and is a minimally invasive therapeutic method.
The advantage is that the incision is avoided here – the classic opening and recovery after the intervention is significantly shortened.
What is an endovascular stent graft?
Endovascular – this means that the intervention is performed inside your aorta using thin, long tubes called catheters. Through small incisions in the groin, catheters are used to guide and deliver the stent-graft through the blood vessels to the site of the aneurysm. The stent is then deployed to the affected aortic segment and “divides” the aorta like a sleeve to divert blood flow from the aneurysm.
An endovascular stent graft is a tube of tissue supported by metal wire stents (also called scaffolds) that reinforce a weak spot in the aorta. By tightly sealing the area with the artery above and below the aortic aneurysm, the graft allows blood to pass through it without pressing on the aneurysm.
Valiant Captivia System
At the Pulse Cardiology Center, these interventions are performed using the state-of-the-art Valiant Captivia system developed by our partners, Medtronic.
The Valiant Captivia system is built on more than 19 years of experience in thoracic stent transplantation. The Valiant stent graft has a unique, durable design that is flexible, adapted to the anatomy of an individual patient and ensures accurate placement.
- Sinusoidal shape and placement of nitinol springs provide flexibility and adaptability.
- Super-elastic nitinol springs exert an active radial force to improve tightness and flexibility.
- Capture of the tips ensures controlled deployment and precise placement in the thoracic aorta.
- Top release lever allows easy rotation and pulling to release proximal stents.
- The crossing profile is similar to or lower than other thoracic stents.
- Hydrophilic coating facilitates stent delivery.
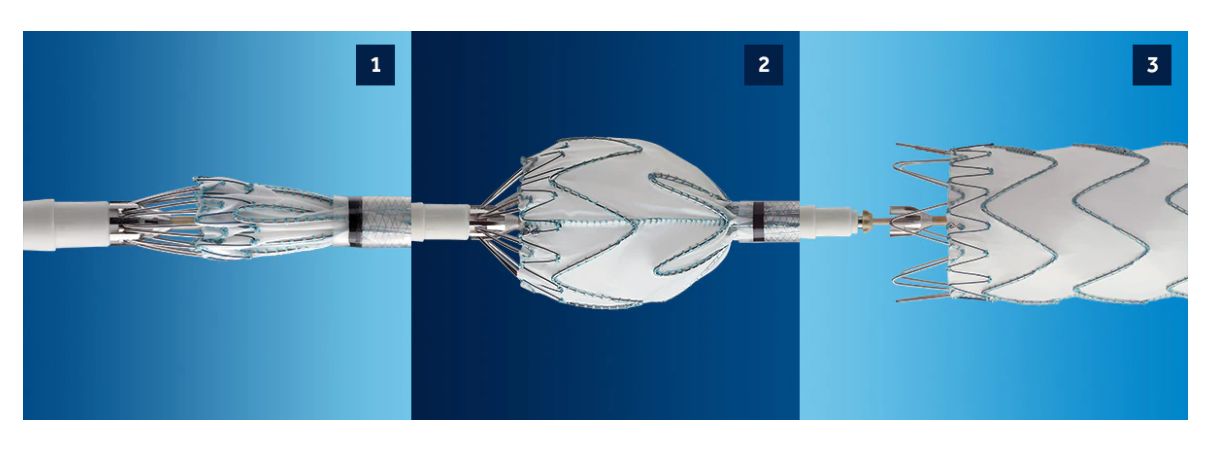
- Simple application process in just three steps.
Who is a candidate for endovascular repair of a thoracic aneurysm
You may be eligible for an endovascular stent graft if the thoracic aneurysm has not ruptured and the aneurysm is 5 centimeters or more in size.
Your doctor can determine if aortic aneurysm treatment is the best treatment option by performing tests and imaging, which may include:
- High resolution CT scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Angiography (X-ray of blood vessels)
- Transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) to take ultrasound images of your heart from the esophagus
- Intravascular ultrasound
The physical characteristics of the aorta and the aortic aneurysm itself are very important in determining whether endovascular aortic repair is the best treatment.
How an intervention is performed to treat a thoracic aortic aneurysm
Your surgeon will make small incisions in the skin above the femoral artery (the large artery that gives blood to each leg) in the groin. The guidewire runs through an artery outside the area of the thoracic aneurysm.
Using X-ray guidance, the surgeon inserts the device over the guide. A stent-graft device is limited inside the catheter to facilitate delivery of the stent-graft through your blood vessels. Once the graft is taken to the site of the thoracic bone aneurysm, the catheter is withdrawn, leaving the stent-graft in the desired location. The stent-graft then expands like a spring to fit into the aortic walls on both sides of the aneurysm and allows blood to flow through the weakened portion.
Once the stent-graft is placed, blood flows through the graft, avoiding the aneurysm. Over time, the aneurysm usually decreases due to the diversion of blood pressure from the aneurysm.
Doctors at the Pulse Cardiology Center also use fenestrated and branched endografts to treat more complex thoracic aneurysms that include the aortic arch and thoracoabdominal aneurysms (those that affect the aorta in both the chest and abdomen). In addition, branched and fenestrated grafts are used to expand thoracic grafts to repair those aneurysms that involve vessels leading to the intestines or brain and arms.
For those patients with extensive aortic or multiple aneurysms, the best approach may require a combination of open surgery and endovascular intervention. This combination therapy is called a hybrid approach.
Risks of thoracic aortic endovascular treatment
Although endovascular surgery reduces recovery time to a few days, there are still potential risks. Possible complications of endovascular repair include:
- Blood leakage around the graft, known as the endoleak
- Moving or migrating the graft from the original placement
- Stent fracture
Additional rare but serious complications include:
- Paralysis
- Delayed aneurysm rupture
- Infection
Your surgeon will discuss the benefits and potential risks of the procedure with you.
Benefits of minimally invasive treatment of the thoracic aorta
Endovascular treatment of the thoracic aorta is generally a less painful procedure and has a lower risk of complications than traditional surgery because the incisions are smaller. Minimally invasive treatment of a thoracic aortic aneurysm also allows you to leave the hospital earlier and recover faster.
Recovery after endovascular treatment of thoracic aneurysm
Your hospital stay after an endovascular stent graft is usually 2 to 3 days. Although your recovery will take less time than recovery from classic thoracic aneurysm surgery, early limitations are similar and include:
- Do not drive until your doctor approves it (usually 1-2 weeks after the procedure and if you are no longer taking painkillers)
- No baths until the cuts on the groin heal; showers and spongy baths around the cut are allowed
- Avoid lifting weights of more than 10 kilograms approximately 4 to 6 weeks after the procedure
You will come for a check-up within a month of the procedure. Subsequent imaging tests will be performed 1 and 6 months after the procedure to determine that the stent is still functioning and in place. If the aneurysm shrinks and no problems are found, your next tests will be done every year.
After endovascular treatment of an aneurysm, it is recommended to adopt the same healthy lifestyle for the heart that other patients with heart surgery lead. Our healthcare team can provide you with more information.
More information about thoracic aneurysm and treatment at the Pulse Cardiology Center
If you need additional information or want to schedule an examination at the Pulse Cardiology Center, you can contact us at: +381117555000 or you can schedule an examination online.
