Heart and cardiovascular diseases have been the leading cause of death in developing countries like Serbia, as well as in the European Union, for decades. Worldwide, nearly 50,000 people die from cardiovascular diseases every day. Angina pectoris and acute myocardial infarction, or heart attack, are the most common cardiovascular diseases in Serbia. Heart attack is characterized by a high patient mortality rate of almost 30%.
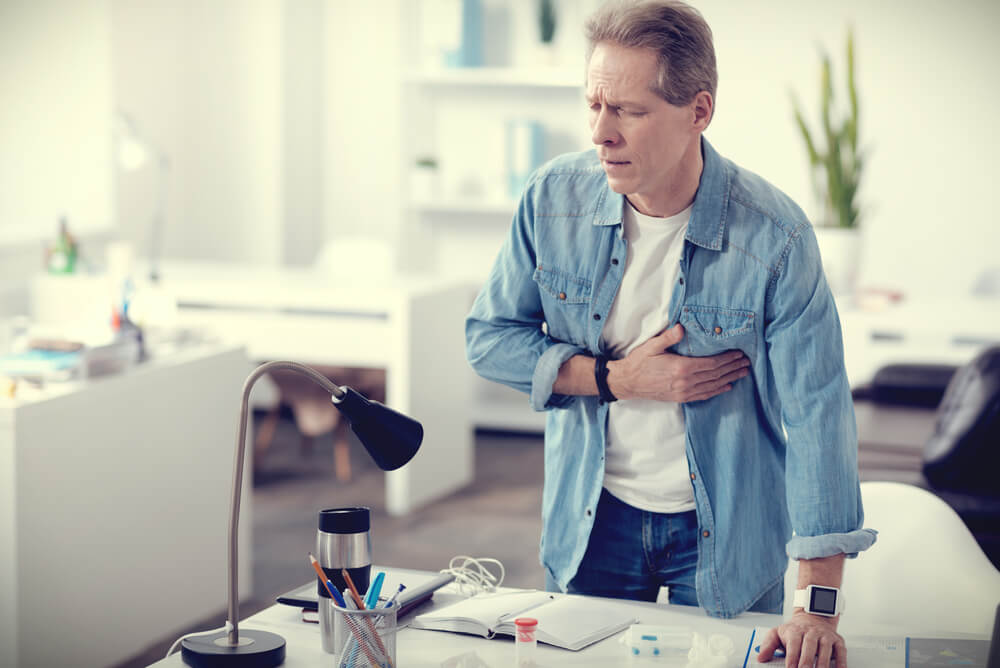
The symptoms of a heart attack usually include a squeezing pain behind the breastbone that spreads to the lower jaw, left arm, and stomach, with increasing intensity. However, heart attack symptoms can also be absent, and the patient may experience a silent or “silent” heart attack. This type of infarction may be accompanied by symptoms that we would not initially associate with heart disease.
In some cases, a silent heart attack may go almost unnoticed, and patients may not even seek out a cardiologist for an examination to determine the extent of damage to the heart muscle. The problem lies in the fact that damage caused by a previous heart attack is a common cause of mortality in cardiovascular patients. Therefore, knowledge of the symptoms of a silent heart attack is crucial for timely patient response and adequate treatment of the resulting health problem.
How to recognize the symptoms of a silent heart attack?
Due to the absence of characteristic symptoms of a heart attack or their manifestation in a milder form, patients with a silent heart attack may only experience minor discomfort. Regardless, a silent heart attack is equally dangerous and accounts for about half of all recorded heart attacks. In addition to intensity, the type of sensations that a patient experiences in this health condition can vary.
An additional problem is the possibility of misinterpretation or more difficult recognition of symptoms. Pain that occurs in the upper abdomen during a silent heart attack can be associated with a feeling of burning in the stomach or heartburn. Increased fatigue or shortness of breath can be attributed to intense physical activity that preceded the onset of these symptoms. Discomfort in the stomach that is attributed to digestive problems, nausea, back pain, or even toothache can be the only sign of a heart attack if characteristic chest pains are absent.
Doctors report that silent heart attack is more common among the male population and is typical for older individuals and patients with diabetes who may only feel fatigue during exertion or difficulty breathing. If they attribute these symptoms to a chronic condition of their body, patients often only find out that they have had a heart attack during routine check-ups with their doctor. Due to the fact that the resulting damage is not adequately treated, these patients are at greater risk of subsequent heart attacks as well as a higher risk of death due to coronary artery disease.
Symptoms of silent heart attack can be of very mild intensity or short duration, causing patients to neglect or attribute them to less serious health conditions or the usual discomfort they sometimes feel. Although silent heart attack is less common in women, the symptoms women experience are less specific and less pronounced, resulting in their higher mortality due to inadequate treatment of the infarction. Increased sweating and heat accompanying the infarction can often be associated with hot flashes, sudden heat attacks characteristic of menopause.
Other health problems in women, such as thyroid dysfunction, can cause irregular heart rate or rhythm disturbances. Women may also feel non-specific pain in the upper body, such as shoulder or upper back pain that is associated with muscle strain or spasm, as well as prolonged and excessive fatigue. Therefore, women may attribute cardiovascular problems to the irregular functioning of other organs or to non-specific disturbances that do not indicate a heart or blood vessel disorder. This reduces the chance for female patients to timely seek a cardiologist and properly manage their health condition.
What are the risk factors for a silent heart attack?
Although there are no diagnostic methods that a cardiologist could use to predict whether a certain patient will experience a silent heart attack, risk factors that can lead to this type of cardiovascular problem are well known. Risk factors for the occurrence of a silent heart attack are the same as those for a heart attack accompanied by characteristic symptoms.
In addition to the already mentioned older individuals and diabetics, at-risk groups also include people with excess body weight, high blood pressure and cholesterol, as well as smokers and physically inactive individuals, especially if they quickly decide to engage in high-intensity training. Individuals who have a family history of cardiovascular disease, i.e., a genetic predisposition, as well as patients who have already suffered a heart attack, also face a greater risk of experiencing a silent heart attack.
Furthermore, certain autoimmune diseases such as lupus significantly increase the risk of heart attack in women, due to accelerated plaque formation in blood vessels and atherosclerosis. Women who develop hypertension and preeclampsia during pregnancy may face weakened heart function and a greater risk of heart attack in middle and old age. Patients with rheumatoid arthritis are also at increased risk of experiencing a heart attack.
When is it necessary to see a cardiologist?
If you belong to any of the mentioned high-risk groups, you should undergo medical examinations that will accurately determine the condition of your cardiovascular system. A cardiologist will make a detailed analysis of the patient’s risk factors and provide appropriate treatment to reduce the chances of developing a silent heart attack and other heart diseases. Do not postpone preventive or regular heart check-ups, especially if you have associated illnesses, because prevention of disease development is always the best option.
However, if you have already experienced some of the previously mentioned symptoms of a silent heart attack, do not ignore them and do not hesitate to visit a cardiologist. The timely reaction of a patient who visits a doctor at the onset of the first symptoms can significantly reduce unwanted consequences and improve treatment outcomes. Even if you do not suspect that your symptoms are related to heart disease, a routine examination by a cardiologist can reveal a heart attack and damage to the heart muscle that requires treatment.
At the Pulse Cardiology Center in Block A of New Belgrade, it is possible to perform a complete diagnosis of the heart with the help of the most advanced equipment, so that you can have an accurate insight into the health of your heart and blood vessels. Schedule an appointment with us, and top-notch experts in the field of cardiology will welcome you in a pleasant environment and provide adequate care for your symptoms so that your heart can receive the treatment it deserves.