The reasons for this mostly lie in some acquired or inherited heart disease, and timely detection has a major role in cardiological examination. Only after a specialist’s examination and necessary analysis will it be possible to define the problem and proceed with its treatment.
Pulse or heart rhythm is very important for the health of our heart. It is extremely important that it is appropriate for the heart to perform its function as a pump. Neither faster nor slower heart rate is usually good for the heart and the patient in general, although sometimes they can be physiological, or harmless. This will, of course, depend on many factors, and only a cardiologist can tell you after a detailed analysis whether your heart needs treatment.
A person can usually feel when their heartbeats deviate from normal because certain symptoms will be present. Especially when there is a real problem in the background that needs to be treated, the signs will be more pronounced. It is up to us to recognize them and seek medical help.
 What is bradycardia?
What is bradycardia?
The normal heart rate for an adult is between 60 and 100 beats per minute. If this number is lower most of the time, the patient probably has bradycardia, while a higher number of beats per minute represents tachycardia.
Not every deviation from the normal number of heartbeats is dangerous to health; for example, athletes and manual laborers often have fewer heartbeats per minute than normal. During sleep, the number of heartbeats can also be lower.
Bradycardia most often occurs due to dysfunction of the sinus node or sick sinus syndrome. The role of the sinus node is of great importance for the proper functioning of the heart. It sends electrical signals and controls the rhythm of the heart. If everything is fine, heartbeats will move in the range of 60 to 100, but if it does not function properly, it can send signals slowly.
In addition, it can happen that the sinus node sends signals at a normal rate, but that due to blockage of the sinus node, they encounter an obstacle. Due to the obstacle, there may be a delay in the electrical signals or complete blockage.
What are the causes of bradycardia?
Slow heart rate is much more common in older people, and age is certainly a risk factor for all heart diseases.
The causes of bradycardia can be different, and among the most common are:
- damage to heart tissue that occurs as a result of aging
- damage to heart tissue that occurred due to some heart disease or after a heart attack
- high blood pressure (hypertension)
- myocarditis – inflammation of the middle layer of the heart wall, which occurs due to viral infection, poisoning by toxins, or due to an autoimmune process
- heart defect present in a person from birth
- complications after heart interventions
- problem with the level of electrolytes
- breathing problems during sleep – apnea
- lupus
- rheumatic fever
- hemochromatosis (a disease that involves the deposition of iron, which causes serious heart, liver, pancreatic and skin insufficiency)
- some medications
Symptoms of bradycardia
In most cases, the patient begins to feel signs and discomfort that may indicate bradycardia only when the heart rate drops below 50 beats per minute.
Then the brain, as well as the rest of the body, do not receive enough oxygen-rich blood, which leads to the following manifestations:
- fatigue
- dizziness or lightheadedness
- fainting
- shortness of breath
- chest pain
- confusion or difficulty concentrating
What are the consequences of bradycardia?
Individuals who have bradycardia and do not receive treatment or follow their doctor’s advice often experience fainting spells. Losing consciousness can happen anywhere, and injuries from falls are also possible. Generally, insecurity and fear of new fainting spells often prompt patients to seek help and begin the process of diagnosing the disease.
The most severe consequence can be sudden cardiac arrest leading to death.
Therefore, precisely because bradycardia can be potentially fatal, it must be diagnosed in time, determined whether treatment is necessary, and the treatment process begun.
Like all other heart diseases, the genetic factor is essential, so if someone in the family has had bradycardia, family members should be vigilant and undergo cardiological examinations earlier and before the onset of symptoms in order to prevent it.
How is bradycardia diagnosed?
Due to the symptoms that characterize bradycardia, which can easily indicate other diseases and problems, the diagnostic process often starts from different points and with different assumptions, and ends up with bradycardia.
Also, very often, in situations when this problem still does not cause discomfort and symptoms that would indicate it, patients, while doing other analyses, find out that they also have bradycardia.
We strive to educate you about the importance of preventive check-ups because they can really bring the most benefit to every person.
Heart diseases in the early stages almost never cause discomfort or any special symptoms. Years can pass before the first signs appear, and your heart has been suffering and endangered for all that time.
It is much easier to treat bradycardia and other heart problems when they are detected in the early stages, when they have not yet left significant traces on the heart.
If a cardiologist suspects bradycardia, he will probably refer you for the following tests:
- Blood tests
Some parameters that can be checked by analyzing blood counts and some hormones can indicate the reasons for bradycardia or the consequences it has had on the body. For example, deviations from normal values of electrolytes or thyroid hormones can provide important information to your doctor.
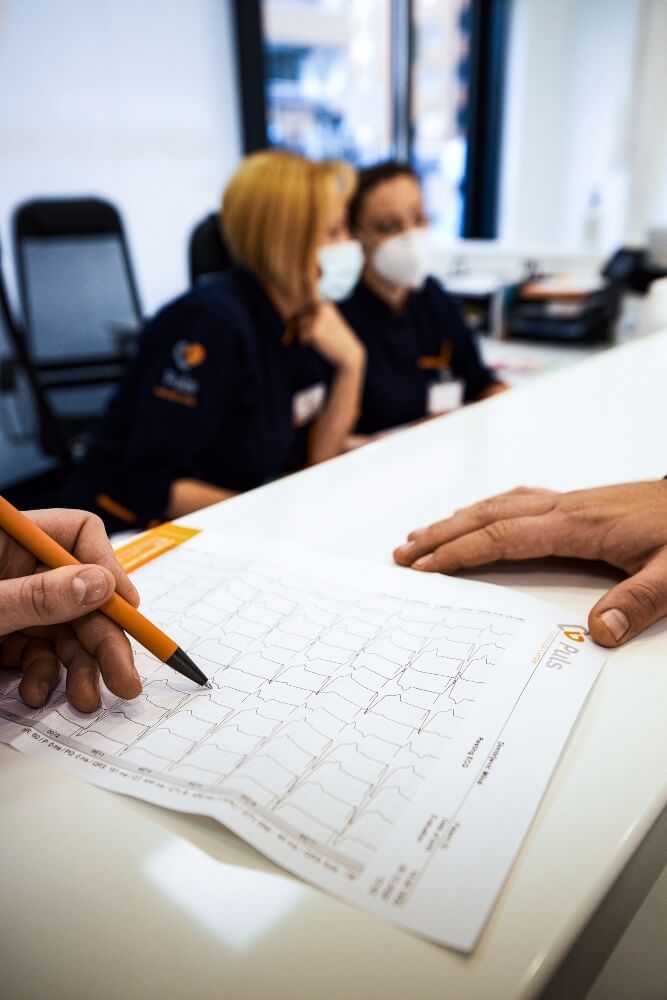
ECG is a diagnostic method that can record the electrical activity of the heart, so it is useful and often used in this situation. What limits this method is the fact that the patient may not have an active disorder at the time of the recording, which is why there are still other recording options, including a 24-hour holter.
This diagnostic method allows monitoring of heart function for 24 hours, providing a much better picture of when irregular heart function occurs, how long it lasts, etc.
- Stress test (ergometry)
The exercise stress test measures heart activity during periods of great effort. The patient usually rides an ergo bike or walks and runs on a treadmill, and for older people, heart rate is increased in a different way since this type of exercise is not suitable for them.
- Echo of the heart (echocardiogram)
Thanks to an echocardiogram, it is possible to see whether a congenital anomaly or other problem is affecting the function of the heart.
How is bradycardia treated?
Sometimes, bradycardia does not require treatment at all. Not all bradycardias are dangerous or life-threatening.
In situations where they pose a danger to the normal functioning of the heart, patients usually have the following options available: using medication to control the heart rate or implanting a pacemaker. Depending on many factors including the patient’s overall health, associated diseases, age, symptoms, and severity of the condition, the doctor will recommend the best option.
Implanting a pacemaker is one of the safest options, but if possible, medication is usually recommended first. Pacemakers are now implanted quickly, do not require a long recovery or hospital stay, and provide a much more carefree life.
The Pulse Cardiology Center has formed an excellent team of cardiologists with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating heart disease, as well as performing a variety of interventions to save lives and improve the quality of life of our patients. If you have any suspicion of a heart condition or simply want to undergo a preventive check-up, call us and schedule your appointment.
The best time for a check-up with a cardiologist is always!