At the Pulse Cardiology Center, it is possible to perform this and other important laboratory tests for diagnosing heart problems. This test is recommended by doctors not only in emergency situations but also for monitoring the effects of treatment and in cases where there is a risk of a heart attack. It can help diagnose both minor and more serious conditions, particularly those considered emergencies.
What is troponin?
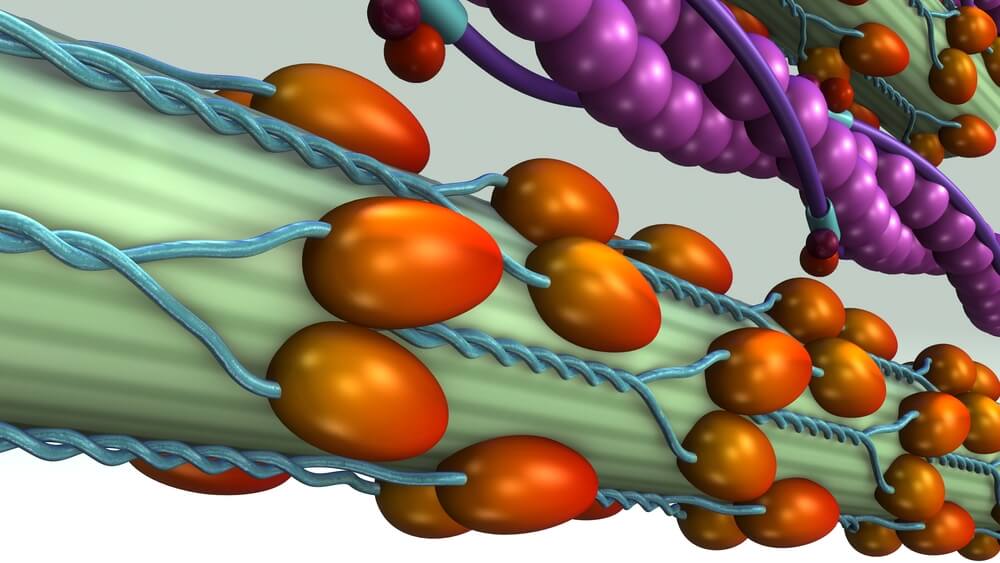
Troponin is the name for a group of proteins that play a crucial role in the heart. Troponin is involved in regulating the contractions of both the heart and skeletal muscles. It is primarily located in skeletal muscles and the cardiac muscle. When there is a problem with the heart, such as a heart attack, troponin is released into the blood, causing an increase in its concentration.
The level of troponin in the blood corresponds to the severity of the heart problem. The greater the problem in the heart, the higher the troponin level.
There are three types of troponin:
- Troponin T (TnT): It is found in both the cardiac and skeletal muscles and is important for muscle contractions. Troponin T connects with other troponin proteins and muscle fibers. In the case of a heart problem, its level increases.
- Troponin I (TnI): It is present in both the cardiac muscle and skeletal muscles, and its role is also related to muscle contraction. Troponin I binds to actin proteins. During a heart attack, its level rises.
- Troponin C (TnC): It has the ability to bind calcium, which leads to a conformational change in troponin, allowing for muscle contractions.
Reference values of troponin
Tests conducted to determine the levels of troponin are highly sensitive, but in healthy individuals, it may not be detected at all. Normal troponin values fall within the range of the 99th percentile, and anything above that is considered elevated and a potential indication of heart damage. Typically, within 3 to 4 hours after an event, the levels of this protein increase and remain elevated even up to 14 days afterwards. It is possible for patients to experience distressing chest pain, leading them to suspect a heart attack, but if the troponin levels do not rise even after 12 hours, it is a sign that an infarction most likely did not occur.
It is important to note that troponin T and I are used as markers for a heart attack, and their levels are measured. If these levels are elevated, it indicates some form of damage. The higher the number on the test result, the greater the impact on the heart. As time passes from the event and treatment progresses, troponin levels will decrease.
What affects troponin levels?
Troponin levels increase when there is damage to the heart, as it is then released from the cardiac muscle into the blood and can be detected through a simple blood test.
However, apart from this primary reason, there are other factors that can influence this protein:
- Sepsis and other major infections
- Intense physical activity
- Burns
- Certain medications
- Kidney diseases
- Cardiomyopathy and heart failure
- Inflammation of the heart lining (pericarditis)
- Inflammation of the heart muscle (myocarditis)
- Inflammation of the heart valves (endocarditis)
- Pulmonary embolism (blood clot in the lungs)
- Diabetes
- Hypothyroidism – decreased secretion of the thyroid gland
- Stroke
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
 When is troponin measured in a patient?
When is troponin measured in a patient?
As mentioned before, when a person presents with symptoms that could indicate a heart attack, obtaining a blood sample and measuring troponin levels is an important step in the diagnosis. The most commonly recognized symptom of a heart attack is severe chest pain or pressure that radiates to the left arm, but it is not the only sign. Prior to a heart attack, a patient may experience fatigue without a reasonable cause for several days, or they may feel extreme weakness just before a heart attack. These symptoms were particularly reported by women, along with sleep problems, even a month before the event.
Dizziness, lightheadedness, shortness of breath, and abdominal discomfort resembling digestive issues are also considered warning signs of a heart attack. Rapid heartbeat and cold sweats can also indicate that something is wrong with the heart. An individual may experience only one symptom or several at once, but it is crucial to recognize one’s condition as dangerous and seek emergency help.
When under the care of experts, it will become clear how they will determine whether you have had a heart attack or not. There were other tests before this troponin analysis, but no other blood test has this level of reliability, which is why it is the preferred choice of cardiologists. Of course, this doesn’t mean that the troponin test alone is sufficient. Together with other diagnostic methods, it can confirm or refute suspicions of a heart attack.
ECG, or more precisely, the measurement of the electrical activity of the heart, is considered a rapid and reliable method for detecting abnormalities in heart function, making it a top priority among diagnostic methods. This way, the doctor can monitor the beating of your heart in real time and identify any irregularities that may be present. An echocardiogram can provide the cardiologist with insights into the morphology and functioning of the heart and cardiac muscles. In cases where this method does not yield satisfactory results, other imaging methods such as X-ray and CT scans are available. Cardiac catheterization, although minimally invasive, is still an invasive method that is also available in this situation. If there is a need to not only visualize the structure of the heart but also measure important parameters, cardiac catheterization would be the appropriate diagnostic step.
How to prepare for a troponin analysis?
No specific preparation is required for this analysis. It should be noted that it is often performed when a patient feels unwell and suspects their life may be in danger. The timing of the blood sample for this analysis is not crucial in terms of selecting an ideal time of day; what matters is the duration since the onset of suspicious chest pain or other symptoms of a heart attack. Troponin levels in the blood increase several hours after the onset of an attack, so measuring it too early may yield falsely negative results. Due to the individual dynamics of troponin elevation in each patient, in accordance with their condition, it is highly likely that this test will be repeated multiple times during the patient’s hospital stay to monitor and assess their condition.
Never leave things to chance, especially when you are aware that you are in a state that requires urgent action. Timely assistance and rapid diagnostics can provide you with prompt and effective treatment, thereby increasing your chances of successfully overcoming a dangerous situation such as a heart attack.
At the Pulse Cardiology Center, we offer everything from basic laboratory tests to advanced and minimally invasive diagnostic methods, as well as life-saving interventions. Take a look at our fantastic team of cardiologists and schedule a consultation even before you experience any symptoms. What you don’t know about your heart can cost you, so preempt unfortunate events through early diagnosis and effective treatment if a problem exists.