What is an ultrasound?
Ultrasound (ultrasonography) is a medical imaging technique that uses high-frequency sound waves to produce images of the body’s internal structures. This technique enables non-invasive visualization of organs, tissues and blood vessels, without the need to use ionizing radiation as is the case with X-ray imaging. The procedure is usually performed using a device known as an ultrasound scanner or ultrasound machine. The scanner emits high-frequency sound waves into the patient’s body and then records the reflection of those waves as they bounce off various internal structures. This information is processed to create images that a doctor can use to diagnose and assess a patient’s health.
Doppler ultrasound (Doppler sonography) is a special type of ultrasound technique that enables assessment of blood flow through blood vessels. In addition to providing static images of internal organs, Doppler ultrasound can detect and measure the speed and direction of movement of red blood cells in arteries and veins. When sound reflects off moving objects, such as red blood cells, the frequency of the sound changes relative to the frequency of the sound that was sent. This change in frequency is used to calculate the speed and direction of blood flow in the arteries and veins. Doppler ultrasound usually shows single-color images (most often red and blue) that represent blood flow direction and speed.
Color Doppler (Color-Doppler sonography) is a more advanced technique that uses the Doppler effect to visualize blood flow in blood vessels in color. In addition to information about the speed and direction of blood flow that is obtained from a regular Doppler ultrasound, Color Doppler adds a visual component. Color images are displayed on the screen indicating the different directions of blood flow. For example, blood moving towards the ultrasound probe is shown in red, while blood moving away from the probe is shown in blue. By combining these colors, the doctor can easily identify normal or abnormal blood flow.
Ultrasound is a safe, painless and non-invasive procedure, so it is often used as the first step in diagnosis before other, more invasive imaging methods or procedures are considered. However, it also has its limitations, as it cannot penetrate bone or air, so it cannot be used to visualize internal structures that are covered by bone, such as the brain or lungs. Also, image quality may be limited in people who are overweight or have gas in the intestines. In those situations, the doctor may recommend other imaging methods, such as computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
Why is an ultrasound performed?
Ultrasound is performed for many reasons in medicine due to its wide applicability and safety. Here are some of the main reasons why an ultrasound examination is performed:
Diagnostics and evaluation of the state of organs: Ultrasound is used to examine various organs, such as the heart, liver, spleen, kidney, thyroid gland, breast, testicles, prostate, uterus and ovaries, in order to identify possible changes, cysts, tumors, inflammations and other problems.
Pregnancy screening
Ultrasound is an essential tool for monitoring fetal development during pregnancy. It allows doctors to assess the size and position of the fetus, detect possible anomalies, assess blood flow through the placenta and monitor the general health of the pregnant woman and her unborn child.
Blood vessel monitoring
Ultrasound is used to assess blood flow through arteries and veins. This is especially beneficial for people with cardiovascular disease or conditions such as varicose veins, thrombosis or narrowing of the arteries.
Management of interventions
Ultrasound can be used as a guide during some medical interventions, such as biopsies (removal of tissue for analysis), drainage of abscesses, guiding of injection needles, and the like. This enables precision and reduces the risk of damage to surrounding structures.
Monitoring development and treatment
Ultrasound can be useful for monitoring the effects of therapy, such as the treatment of tumors or cysts, and provide information on the progress of treatment.
Detection of soft tissue problems
Ultrasound can detect inflammatory processes, abscesses, cysts and other soft tissue changes that cannot be seen on standard X-rays.
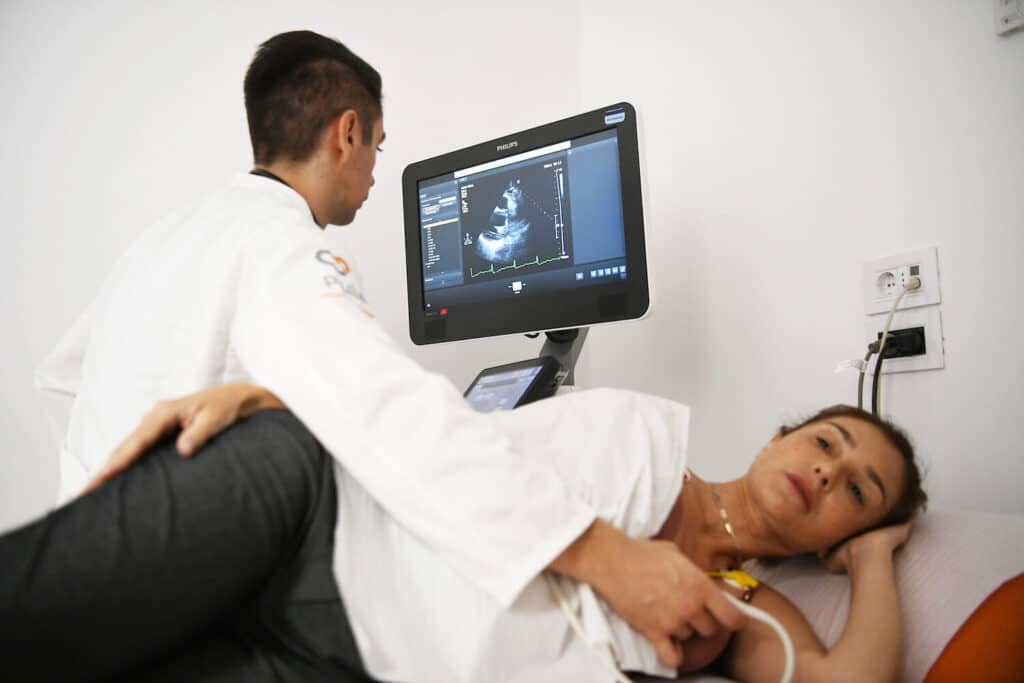
What are the types of ultrasound?
Ultrasound examination of the heart
Color doppler neck blood vessels
- Evaluation of circulation in the carotid arteries to identify possible narrowings (stenosis) or other problems that may increase the risk of stroke.
- Assessment of venous circulation in the neck region to identify varicose veins or other problems in the venous system.
- Identification of blood clots (thrombi) in the blood vessels of the neck, which is important for early detection and prevention of complications.
Color Doppler of the lower extremities blood vessels
Color Doppler of the upper extremities blood vessels
- Assessment of blood flow in the arteries to identify possible narrowings (stenosis) or blockages that may cause circulation problems.
- Assessment of venous blood flow to identify enlarged veins (varicose veins) or vein problems.
- Identification of blood clots in the blood vessels of the arms and legs, which is important for early detection and prevention of complications such as deep vein thrombosis or pulmonary embolism.
Color Doppler of the abdominal aorta with visceral branches
Ultrasound examination of the thyroid gland
- Evaluation of the size and structure of the thyroid gland
- Detection of cysts, nodules and other changes
- Monitoring thyroid conditions over time, as well as to monitor the progress and effectiveness of treatment in patients with certain conditions, such as thyroid disease.
- Guide to taking tissue (biopsy) for further analysis and making an accurate diagnosis
- Transabdominal ultrasound
- This is the most common type of ultrasound. With the help of transabdominal ultrasound, an ultrasound probe is placed externally on the skin of the patient’s abdomen in order to examine the internal organs, such as the liver, kidneys, spleen, uterus, ovaries and bladder. Ultrasound of the abdomen, urotract and small pelvis is a comprehensive diagnostic procedure that combines ultrasonography to visualize and evaluate organs in the abdominal cavity, urinary system and reproductive organs in the pelvic region.
Abdominal ultrasound
- Visualization of the liver: Ultrasound allows examination of the liver to detect changes in size, structure, fatty infiltration, cysts or tumors.
- Evaluation of the gallbladder and bile ducts: Ultrasound is used to examine the gallbladder and bile ducts to detect possible stones, inflammation, or other changes.
- Examination of the spleen: Ultrasound allows examination of the spleen to identify changes in size, structure or possible tumors.
- Evaluation of the pancreas: Ultrasound is used to examine the pancreas to detect any changes, cysts, or tumors.
- Examination of the kidneys and bladder: Ultrasound allows examination of the kidneys and bladder to detect possible changes in size, shape, presence of stones, tumors or other problems.
- • Visualization of the intestines: Ultrasound can help detect possible problems in the intestines, such as diverticula, cysts, tumors or inflammation.
Ultrasound of the urinary tract
- Assessment of renal structures: Ultrasound enables an examination of the renal parenchyma (internal tissue of the renal organs), its size, position and possible changes, such as cysts or tumors.
- Bladder visualization: Ultrasound is used to examine the inside of the bladder to identify possible inflammation, the presence of stones or other pathological changes.
- Monitoring urine flow: Using Doppler ultrasound, doctors can assess the flow of urine through the ureters and monitor possible narrowings or blockages.
- Detecting problems in the urethra: Ultrasound can help detect possible strictures or other problems in the urethra.
Pelvic ultrasound
- Evaluation of the reproductive organs in women: Ultrasound enables examination of the uterus, ovaries and surrounding structures. This technique is useful for detecting problems such as cysts, fibroids, tumors, inflammation or other gynecological conditions.
- Prostate evaluation in men: Ultrasound is used to examine the prostate, which is especially important for detecting potential problems such as prostate enlargement, benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), or prostate cancer.
- Visualization of the bladder: Ultrasound enables examination of the inside of the bladder in order to identify possible inflammation, the presence of stones or other pathological changes.
- Evaluation of the bowel and other structures: Ultrasound can help detect problems in the bowel, such as diverticula, cysts, tumors or inflammation.
Transvaginal ultrasound
Transrectal ultrasound
Color Doppler of renal arteries
Transcranial Doppler (TCD)
- Monitoring blood circulation in the brain in patients with brain injuries, strokes, cerebrovascular diseases, or other neurological disorders.
- Identification of stenosis (narrowing) or occlusion (closing) of blood vessels in the brain.
- Detection of possible emboli (blood clots) in intracranial arteries.
- Assessment of reactivity of brain blood vessels in patients with cerebrovascular disorders.
- TCD is a painless, quick and safe procedure that provides important information about the blood flow in the brain, which is essential for the proper diagnosis and treatment planning of neurological conditions.
Ultrasound examination of the breast
- Identification of breast cysts
- Detection and monitoring of breast tumors
- Follow-up as part of mammographic screening
- Guide to taking tissue (biopsy) for further analysis and making an accurate diagnosis
How to prepare for an ultrasound?
Preparation for ultrasound depends on the type of examination that is planned. Before going for an ultrasound scan, always check with your doctor or healthcare provider for specific preparation guidelines for your specific scan. Proper preparation will help ensure accurate results and facilitate the review process.
Here are some general guidelines that apply to most ultrasound exams:
Educate yourself about the exam: Talk to your doctor or medical staff to find out exactly what you need to do before the ultrasound exam. They will provide you with specific guidelines according to the type of examination scheduled.
Tell your doctor about your medical condition: Before your examination, be sure to tell your doctor about your medical condition, medical history, and any medications or supplements you are taking. This is important so that the doctor can take into account all relevant information during the examination.
Fasting on an empty stomach: In some cases, such as an abdominal ultrasound, you may need to fast before the examination. This means that you will be instructed not to eat anything or drink liquids for several hours before your appointment. This usually involves examining organs such as the liver, gallbladder and pancreas.
Wear appropriate clothing: It is recommended to wear loose and comfortable clothing that can be easily removed or moved if access to the part of the body being examined is required. In some cases, you may be offered a hospital gown during the examination.
Remove jewelry: It is recommended that you remove all jewelry and metal objects before the ultrasound, as they can interfere with the quality of the image on the screen.
Follow instructions: If your doctor has given you special instructions or medications to take before the exam, be sure to follow them carefully.
Relax: Ultrasound is a non-invasive and painless procedure. There is no need for special preparations in terms of taking analgesics or sedatives, unless they have been prescribed by your doctor.
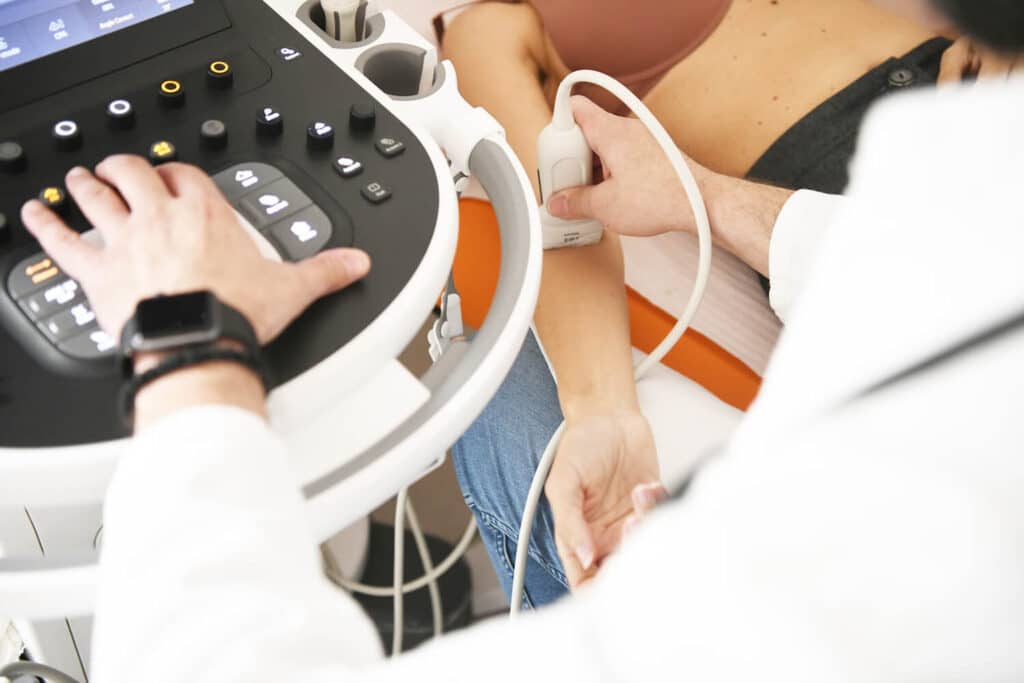
How does ultrasound work and how is the procedure performed?
What are the potential risks of ultrasound?
- Does not use ionizing radiation: Ultrasound uses high-frequency sound waves, not ionizing radiation like X-rays or computed tomography (CT). This means that patients are not exposed to the harmful effects of ionizing radiation during an ultrasound examination.
- It is non-invasive: Ultrasound is performed externally, without the need to insert instruments into the body. This means that there is no need for a needle, catheter or invasive procedures, which reduces the risk of infection or other complications.
- It is painless: Ultrasound waves are painless and do not cause discomfort during the examination.
However, it is important to note that the potential risks of ultrasound are minimal, but there are some minor factors that can be taken into account:
- • Errors in interpretation: The results of an ultrasound examination can depend on the skill and experience of the ultrasound technician and the doctor performing the examination. Errors in interpretation can lead to an incorrect diagnosis, but such situations are rare.
- • Poor visualization: In some patients, ultrasound may be difficult if there is excess fat, intestinal gas, or other factors that reduce visualization of internal organs.
What can the ultrasound results show?
Size, shape and structure of organs
Details inside organs
Blood circulation
Organ function
Detection of pathologies:
Who interprets the ultrasound results and what are the next steps?
- Diagnosis: Based on the ultrasound findings, the doctor can diagnose or rule out certain conditions. In some cases, an ultrasound may be sufficient to confirm certain diagnoses, while in other cases additional testing may be needed to reach an accurate diagnosis.
- Recommendation for additional tests: If the ultrasound reveals certain changes that require further investigation, the doctor may recommend additional tests or diagnostic procedures to clarify the situation and make an accurate diagnosis.
- Therapy planning: Based on the ultrasound results, the doctor can recommend the appropriate treatment or therapy for the patient. These may include medications, surgery, dietary changes, or other therapeutic approaches, depending on the diagnosis.
- Monitoring: In some situations, ultrasound can be used to monitor the condition over time to assess the progress of therapy or changes in the patient’s health.
- Consultation with other specialists: If the ultrasound reveals changes that require the expertise of other specialists, the doctor can refer the patient to a consultation with the appropriate specialists.
Ultrasound diagnostics in Puls Cardiology Center
