It can help detect and monitor diseases that involve narrowing of blood vessels, heart rhythm disorders, hidden disorders of the heart functioning that cannot be noticed during rest. In addition, it is used in situations when it is necessary to monitor the effects of treatment or to check the success of invasive methods such as stenting and balloon expanding.
What is ergometry?
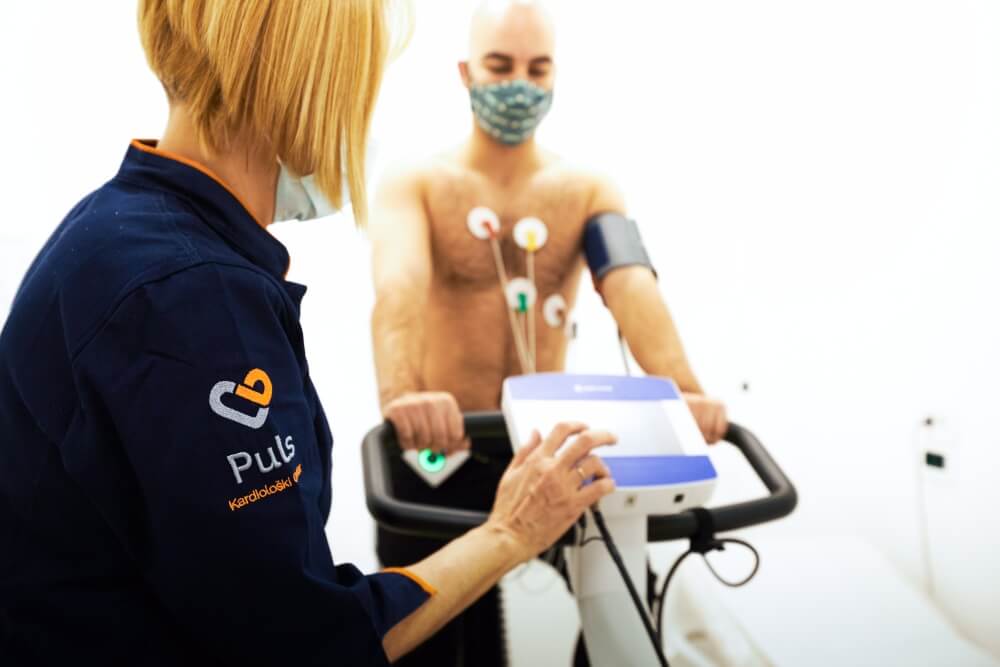
Ergometry or ergo test is a method that involves exposure to physical activity and monitoring its impact on the heart.
This method is non-invasive, the test itself lasts about half an hour, and is performed on a treadmill conveyor belt or ergobicycle, gradually increasing the speed and resistance of the bike or the inclination of the belt.
Is preparation required before the ergo test?
You need to know a few facts to better prepare for this test:
● Regular therapy should be taken before ergometry, unless the doctor says otherwise
● Alcohol, cigarettes, carbonated beverages, caffeinated beverages should not be consumed before the test
● You should eat a light meal two or three hours before
● If you are diabetic, you should take regular therapy before the test and eat a light meal a few hours earlier, and consult your doctor about the amount of insulin you will take
● If you use pumps, bring them
● Wear appropriate clothing and footwear to make you feel more comfortable
● Relax
How is the ergo test performed?
The patient rides an ergocycle or walks on a treadmill walking belt with a gradual increase in physical load, and all the time he is under the strict supervision of experts. It is not crucial for the validity of the test whether the patient used a treadmill walking belt or an ergobicycle, because both aids have a similar role.
In the first two or three minutes the load is 25W, then every few minutes the load increases by 25W. In younger people, the initial load can be twice as high, it all depends on the patient.
During the load test, the electrical activity of the heart is monitored (using an ECG), blood pressure is measured, the number of heartbeats per minute is monitored, breathing, but also how the patient feels. If the patient concludes that he or she cannot, does not want to continue testing, or begins to feel discomfort such as dizziness, choking, heart skipping, and fainting, the test will be discontinued.
The level of load that will be used on the test depends on the patient’s condition. The maximum load test does not always apply. The height that we call submaximal is most often reached, and it implies 85% of the maximum pulse for years of age and a half. A symptom-limited test is also often used, which involves stopping when the relevant symptoms appear.
In heart patients who survived a heart attack in the first three weeks, only a low-load test can be used, and only after six to eight weeks is a test limited to symptoms.
Sensitivity- the sensitivity of this test is between 60% and 70% and depends on the number of coronary arteries involved. In the case of two or three narrowings of the main coronary arteries, the sensitivity of the test will be over 90%.
After the test, the patient will be in a standing position for a few seconds, after which he will lie down for five minutes. During that time, his blood pressure, heart rate per minute will continue to be measured, and the electrical activity of the heart will be monitored.
In our institution, this test is performed in a specially equipped laboratory. The atmosphere is pleasant, the room is bright and ventilated to make you feel as comfortable as possible during testing. At all times, the medical staff has unhindered access to the patient and can react in case of unforeseen situations.
Test results
You get the results immediately after the test.
What is considered a normal reaction to this type of load is a progressive increase in systolic pressure to a value of 160 to 200 mmHg, and these values may be higher in elderly patients. Diastolic blood pressure in healthy individuals does not change significantly during exercise.
If necessary, after the analysis, you will receive therapy and you will be recommended a further course of treatment.
Who is a candidate for ergometry?
People who have symptoms that indicate the existence of coronary problems should undergo this test. Symptoms include high blood pressure, chest tightness, chest pain at rest and during physical activity, shortness of breath.
In addition, if someone has a predisposition to develop coronary heart disease, this test may be recommended, even if no symptoms are present at the moment. It will also be recommended to some people because of their lifestyle, harmful habits or if they are engaged in some stressful occupation.
Diabetics belong to the risk group for the development of coronary heart disease, so they are often referred for a test for control and monitoring.
Some sports medicine specialists believe that all women over the age of 50 and men over the age of 40 should take a load test if they plan to engage in more intense sports activities.
Ergometric test for athletes
Ergometry has also found application in sports due to the nature and quality of the information it can provide to athletes. This test gives them the necessary data on energy consumption, and based on it, it is possible to make a better and more efficient exercise plan, which further leads to better results and injury prevention.
Who is not a candidate for ergometry?
People with certain cardiac problems will not be good candidates for this test:
● Patients with moderate or severe aortic stenosis
● Patients who have inflammation such as pericarditis, myocarditis and endocarditis
● Persons with uncontrolled atrial fibrillation
● People with cardiac decompensation (heart failure)
● People who for any reason do not feel ready to take the test

Is ergometry risky?
The Ergo test is a low-risk test, but the patient receives detailed information about the importance and purpose of this method, as well as the possible risks, before performing the test, after which the consent will be signed. The way someone will undergo an ergo test depends on the symptoms they have and the condition they are in. Not every patient will be exposed to the same physical load, nor is there a need for that.
The test is most often performed in an outpatient setting, as most people who undergo this type of testing belong to low-risk groups.
If a person belongs to a high-risk group for the development of side effects during the implementation of this method, and it is important to apply it, then hospital conditions would be necessary so that professionals can react quickly and appropriately in a critical situation.
Side effects can include a drop in blood pressure, heart rhythm disorders and a heart attack, but they are very rare.
We also mentioned that a contraindication for doing the test may be how the patient feels subjectively. If for some reason he does not feel ready or is afraid, the test should be postponed, because fear and stress can affect the accuracy of the results.
To avoid procrastination and develop unnecessary fear of this method, consult and talk to experts from our team. They will assess whether you are a candidate for testing and what your options are-to what degree of workload it is necessary to go during the procedure. Be sure that you are in safe hands under their supervision.
Regardless of the reason why you need this type of test, you should know that the best service is waiting for you at the Pulse Cardiology Center, which includes a minimum waiting time and a highly professional approach to each patient based on his requirements and specific health condition.