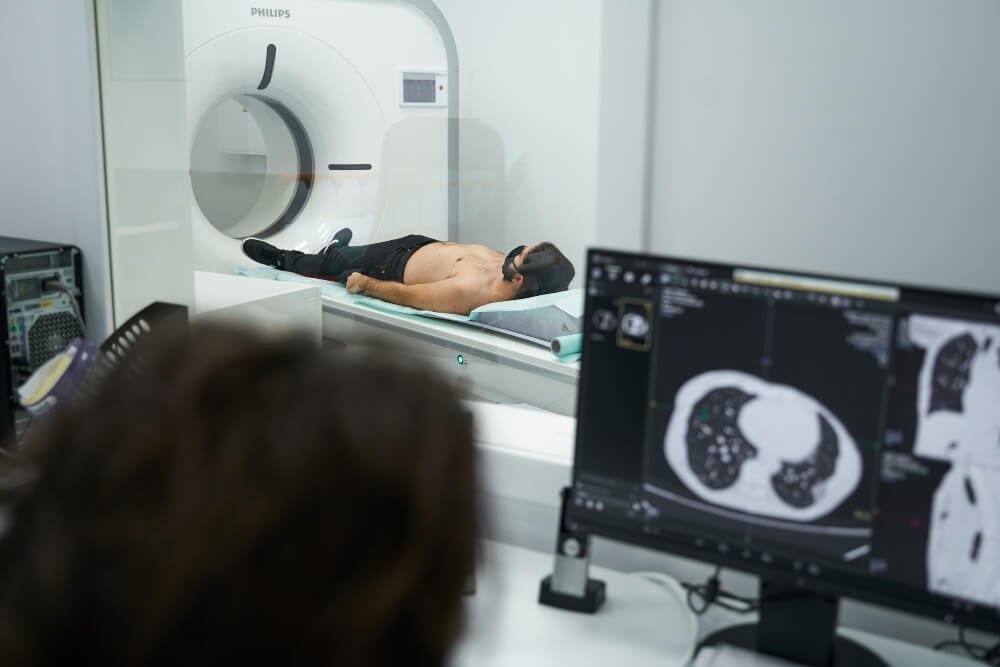
What is CT coronarography?
This method is used for the purpose of diagnosing coronary disease and involves the use of X-rays, the latest technology, and a contrast dye in order to obtain the most accurate images of the coronary arteries.
Thanks to CT coronary angiography, it is possible to determine the place and amount of plaque in the blood vessels. Plaque is a deposit made of fat, calcium and cellular debris that can seriously threaten the free flow of blood and oxygen through the coronary arteries. In cases of major or complete blockage of these arteries, a heart attack can occur.
Diagnosing coronary disease is significantly facilitated by the use of a CT machine and contrast material that is given to the patient intravenously. Thanks to the contrast, the images of blood vessels are much clearer and more precise.
This is a non-invasive, painless, and extremely reliable method. This recording is very comfortable for the patient and takes only a few minutes.
When to perform CT coronary angiography?
Doctors recommend this procedure most often in the following situations:
- when the patient has been determined to have a low or medium risk of developing coronary disease
- when patients have symptoms of coronary disease
- when patients feel atypical chest pain
- when the patient has chronic chest pain
- when other diagnostic tests are inconclusive
- when the patient’s condition worsens despite good stress test results
- when the patient has an implanted bypass
It is not rare that when applying this method, some other problems that the patient may have are discovered, such as: thrombus, lung atelectasis, abnormality of the aorta.
How is CT coronary angiography performed?
Coronary artery imaging is performed in a room equipped with a CT scanner under the watchful eye of a radiologist and X-ray technician.
No special preparations are required before the procedure, but you must tell the doctor if you are pregnant, have kidney disease, are diabetic, or are allergic to iodine, because iodine is part of the contrast material. Even all of this does not mean that you will not be able to be filmed, only that the precaution will be greater or that other specialists will be involved in the final decision.
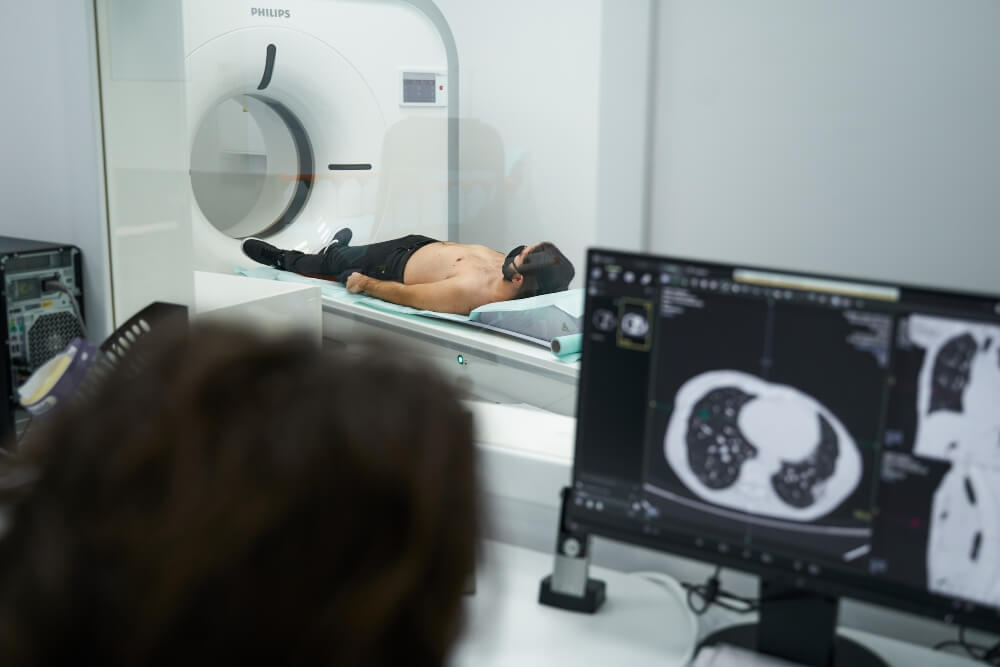
The CT scanner is in the form of a tube into which the patient’s bed is inserted. There is a cavity on both sides and the opening itself is not deep, so the recording should not cause fear and discomfort to the patient. If necessary, the patient is given contrast, after which he is placed in the optimal position for imaging.
All the time the recording is taking place, it is possible to communicate via intercom with the technician or radiologist who are monitoring the process from another room. They are there to make sure the shoot runs smoothly and to reassure you and advise you on what to do if needed.
We use a 128 multi-slice Incisive CT Phillips scanner, a device of exceptional precision. You receive the results of CT coronary angiography immediately, as well as instructions for further steps, if necessary.
This procedure is often recommended by doctors because:
- thanks to it, it is possible to record soft tissues, blood vessels and bones at the same time, so it is more likely that the reason for the patient’s complaints will be discovered, if it turns out that the problem is not the coronary arteries
- the resulting recordings are very detailed and precise, so it is possible to see even the smallest changes
- is a non-invasive method, which means that the patient does not feel pain and discomfort
- the machine is not as sensitive to the movement of the person being recorded as magnetic resonance imaging
- having an implanted device such as a bypass is not a contraindication
- it is one of the faster and simpler procedures, after which patients immediately return to their daily activities
Is this a risky procedure?
Using a CT scanner involves exposure to radiation that is higher than, for example, when you take a picture of a part of the body with a classic X-ray machine. However, CT scanner and the rays it uses should be used sensibly, there should be no health consequences. It is certainly not a diagnostic method that you will use often, but only when needed.
Also, it should be noted that CT coronary angiography belongs to the non-invasive methods of exceptional precision, which is certainly due to the results it provides, it is classified as a purposeful and very important diagnostic method.
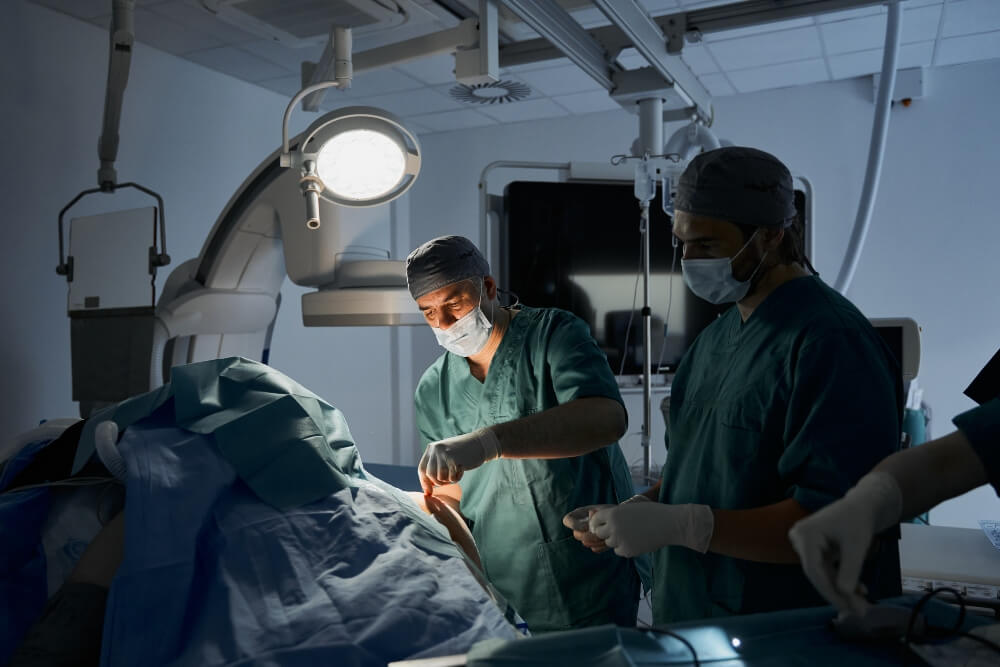
What is cardiac catheterization?
Cardiac catheterization or coronary angiography is an invasive procedure that is used for a number of reasons. Thanks to it, an accurate diagnosis of coronary disease is possible, but it is also used for the purpose of treatment or treatment planning.
The method itself involves the introduction of a catheter through a vein on the arm, neck or groin to the heart in order to measure the pressure in the arteries, ventricles, determine the amount of plaque or to place a stent. Sometimes it starts with the goal of diagnosis, and during the procedure it turns out that the problem is more serious, that the blood vessel is threatened due to the amount of plaque, so it is possible to implant a stent immediately after the discovery.
By implanting a stent, expansion of the narrowed blood vessel is achieved and normal blood flow is established. The stent stays in place permanently.
When to perform cardiac catheterization?
This procedure is performed in the following situations:
- after a heart attack, at the place where the blockage in the blood vessel occurred
- when it is necessary to measure how much blood the heart pumps per minute
- in order to detect tumors that affect the work of the heart
- when it is necessary to determine the existence of some cardiac anomalies
- for diagnosing coronary disease and the amount of plaque on the walls of blood vessels
- to diagnose angina
- it is also important for planning future interventions and ways of treating heart diseases
How is cardiac catheterization performed?
Catheterization of the heart is an invasive procedure, the performance of which requires a specially equipped room, which we call the Cath-lab. In the Pulse Cardiology Center, there is a modernly equipped Cath-lab where numerous diagnostic methods and interventions can be performed.
During this intervention, the patient is awake, but under sedation that allows him not to feel pain and discomfort. A specialist doctor (usually an interventional cardiologist or an interventional radiologist) chooses the appropriate place through which he will introduce the catheter into the blood vessel, which is most often on the patient’s neck, arm, or groin. Once the catheter is inserted, its movement can be monitored on the monitor all the time. The contrast material plays a big role here as well because it helps to see the blood vessels and the constrictions on them in detail.
Depending on what the goal of catheterization is, it can go by different names.
Percutaneous coronary intervention or angioplasty involves catheterization aimed at cleaning a narrowed or blocked blood vessel. Valvuloplasty is the name indicating that the goal of catheterization is to widen the narrowed opening of the heart valve. In addition to all that, we remind you that it is extremely often used only for diagnostic purposes.
After the coronary angiography – catheterization, the patient remains in the hospital for a few more hours, and if a procedure such as stent placement was performed, the patient should also spend the night in the observation ward.
Is this a risky procedure?
This method does not carry great risks. Bruising may occur at the site of catheter insertion, an allergic reaction to the contrast agent is rare, and very rarely blood vessel damage or a heart attack or stroke may occur.
Both procedures that we have brought to your attention in this text are very reliable and safe. Which method will be a better option for diagnosis will depend on the patient’s condition and a number of other things.
After the CT scan, the patient immediately resumes his daily activities, while after the method that involves the introduction of a catheter, this is not possible immediately, but in a few hours, if the patient does not report any discomfort, he can go home accompanied by a long person.
The main difference is that CT coronary angiography is only a diagnostic method, and cardiac catheterization, as an invasive diagnostic procedure that involves the introduction of a catheter into the patient’s blood vessels, can turn into a life-saving intervention.
When the catheter is in the blood vessels, it is possible to immediately introduce other instruments through it, for example to perform a biopsy, measure pressure or implant a stent.
Thus, catheterization offers more application possibilities, but it does not mean that it will always be the right choice. A specialist in cardiology is the only one who can give you the right guidelines, and the best cardiologists in Serbia are in our institution. Schedule a consultation with us by calling the call center at 0117555000.