Interview with Dr. Svetislav Mališić
What are the most common cardiovascular diseases in our population?
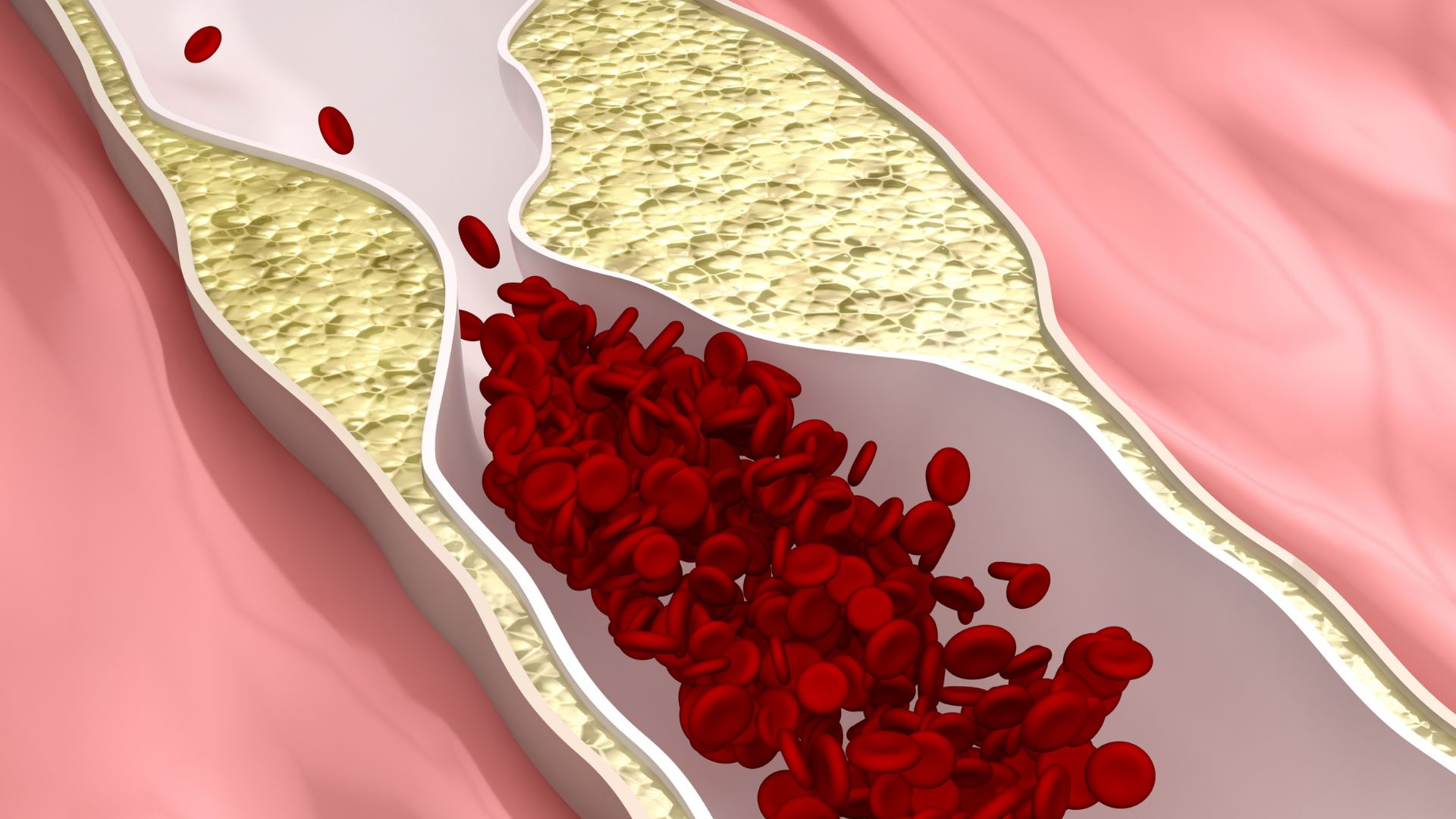
The most common cardiovascular diseases not only in our country but also worldwide are, first, ischemic heart disease (coronary artery disease, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris), second, heart failure, and third, arrhythmias, the most common disorder of heart rhythm precisely in these two groups of patients with ischemic heart disease and heart failure.
According to research, Serbia is in third place in Europe in terms of incidence and mortality rates of cardiovascular diseases. What is the cause of this statistic?
Ischemic heart disease and heart failure are very common not only in Serbia, but also all over the world, precisely because of the way of life. Modern man today pays very little attention to how he eats, what is the level of physical activity. Usually, these are people who are exposed to stress, do not have enough time for some healthy habits (adequate nutrition, physical activity), and in addition, there is consumption of alcohol, tobacco, narcotics, etc. All of these are very significant risk factors that will, regardless of age, sooner or later lead to the occurrence of some cardiovascular disease.
Our fellow citizens do not go for regular preventive cardiology check-ups. It often happens that “someone just collapses” or has a heart attack…
This is related to people’s health awareness. Our average person is not aware that they should visit their doctor at least once a year, even if they have no complaints or problems, to undergo a routine physical examination. Blood pressure, auscultation, ECG – these are simple tools that are available everywhere, from primary health care to tertiary institutions.
What are cardiac arrhythmias?

Arrhythmia – the word itself suggests that something is not in rhythm. The heart has its own internal electrical structure called the sinus rhythm. Sinus rhythm is the physiological, regular heart rhythm, where the heart regularly sends electrical impulses to the cardiac chambers, leading to synchronous contraction of the left and right sides of the heart. When there are various disturbances in this process, it leads to the appearance of an asynchronous or uneven heart rhythm, which the patient feels as symptoms. Patients usually complain of heart palpitations or fast/irregular heartbeats (palpitations). It often happens that people start to “feel their heart.”
Can arrhythmias be cured or is lifelong therapy required?
Ablation is the most modern form of treatment for arrhythmias, known as electrophysiological therapy. These are called radiofrequency ablations, which achieve a cure in a large percentage of cases. Sometimes, after RF ablation, it may be necessary to continue with medication therapy until the doctor gives a different assessment.
Do arrhythmias occur exclusively due to some heart disease?
In most cases, yes. However, this is a very broad area in cardiology that is becoming increasingly recognized as a separate entity – arrhythmology. It is a very complex field, both for diagnosis and treatment. Arrhythmias are most commonly found in patients who already have some structural organic heart disease. However, there are also so-called physiological cardiac arrhythmias that do not require special diagnosis and treatment, and they are also present in the pediatric population, where respiratory sinus arrhythmia is most common. The difference between pathological and physiological arrhythmias is that physiological arrhythmias do not require special attention, unlike pathological ones, which require further diagnosis and treatment.
Does the younger population suffer from arrhythmias?
Yes, the younger population also has problems with arrhythmias.
When it is determined that a patient has an arrhythmia, what diagnostic procedures are used to determine the cause of this problem?
A basic physical examination with a stethoscope, blood pressure monitor, and ECG machine is sufficient to determine whether a patient has a physiological/pathological arrhythmia. Depending on the findings obtained during the initial examination, additional tools are included in the diagnosis. In cardiology today, we have a large number of modern diagnostic tools available, including echocardiography and 24-hour Holter monitoring. For persistent arrhythmias that cannot be detected by conventional Holter monitoring, there are so-called loop recorders that are implanted under the skin and which patients wear for months or even years to detect the type of rhythm disorder. In these situations, there are more complex arrhythmias that are potentially life-threatening.
Modern cardiology has such capabilities that it is simply impossible not to detect cardiac rhythm disturbances.
So, an arrhythmia can be detected on a basic cardiology exam?
Of course, what the patient needs to know is that they shouldn’t neglect their symptoms. We can understand this if the arrhythmia occurs sporadically or has a benign character (it occurs with changes in weather, fatigue, lack of sleep, higher consumption of alcohol and tobacco, or food). However, if the arrhythmia becomes chronic and starts giving subjective symptoms such as fainting spells, then there is no place for waiting.
What is the therapy for arrhythmias?
The therapy for arrhythmias is very complex, just like the diagnostics. Nowadays, we have a wide range of antiarrhythmic medications available, from basic (such as beta-blockers) to the strongest, so-called reserve antiarrhythmics, which we use. Since this is one part of the therapeutic procedures related to pharmacological agents, we also have some non-pharmacological measures, invasive procedures such as radiofrequency catheter ablation in the treatment of complex cardiac rhythm disorders. Of course, there are also pacemakers.
A pacemaker is a device that a person with a serious cardiac rhythm disorder cannot live without. They all have their specificities, as well as specific indications.
Is obesity a significant risk factor for developing cardiovascular disease?
Obesity is not only a burden for the spine but also for the heart. Obesity is the main risk factor for developing hypertension, in addition to which elevated levels of sugar and fats in the blood are usually present. If smoking and alcohol consumption are present, then the person falls into the high-risk category for developing some cardiovascular disease in the next ten-year period. It is not my intention to scare anyone, but people must take seriously the messages that we doctors send at all these meetings, congresses, symposia. We present the results of the latest research and studies where the correction of bad habits, elimination of risk factors, and so-called non-pharmacological treatment measures are unequivocally placed at the forefront at all times. And not only for arrhythmias, but also for the prevention of ischemic heart disease, heart failure, atrial fibrillation, and all other cardiovascular diseases. If these measures do not yield results, then pharmacological measures are used.
What happens to patients who occasionally feel arrhythmias? How dangerous are they?
If those arrhythmias are not accompanied by general symptoms, i.e. if the patient only feels that their heart beats irregularly, it is not dangerous. If symptoms of instability, dizziness, loss of consciousness or a crisis of consciousness occur, they are life-threatening heart rhythm disorders that require detailed investigations in hospital conditions.
Does every arrhythmia require a doctor’s visit?
As we mentioned at the beginning, there are arrhythmias that do not require treatment, for example, diseases of the thyroid gland are very common in women. We must not forget that the thyroid gland can cause significant problems related to heart rhythm disorders (accelerated/slowed heart rate, absolute arrhythmia, etc.). As we said at the beginning, physiological arrhythmias do not require special attention, but we should not relax either. If arrhythmias recur, it is necessary to do certain sets of tests to exclude that secondary cause of arrhythmias (thyroid gland, anemia, hormonal disorders in women, gynecological disorders, women in perimenopause, etc.).
We talked about the importance of prevention, why is it important for arrhythmias?
Prevention of arrhythmias is based on a responsible approach from both patients and doctors. If we have a complex patient with structural heart disease, they will inevitably have some kind of heart rhythm disorder that needs to be treated.
Prevention is important for young people, who need to adopt healthy habits and think about the consequences of their behavior in the future, i.e. in old age.
How often should you go for a cardiology check-up?
It depends on various factors, but my recommendation is that if you are healthy and without symptoms, you should do it every one to two years.
How important is the role of genetics?
Genetics can play a crucial role in some situations, especially when it comes to ischemic heart disease and heart failure.
Besides genetics, it is very important to:
- Eliminate risk factors
- Regularly attend check-ups
- Take therapy regularly
Prevention is the key to good health.
MD. Svetislav Mališić, a cardiologist at Pulse Cardiology Center, has extensive experience in cardiovascular diagnostics and has successfully treated patients with cardiovascular disease for over 16 years.