The consequences of untreated blockage of blood vessels can be stroke and heart attack, which often lead to death.
Thanks to the existence of stents, many fatal outcomes have been avoided and patients have been given a new opportunity to improve their lives.
Life with a stent implies introducing changes in daily habits, not so much because of the stent itself that remains in the body, but because of the prevention of new complications and blockages that are directly related to the patient’s diet and activities.
If you are preparing for this intervention or know someone who has been recommended or has already had it done, read the following lines carefully to learn what a stent is and what life with it entails.
What is a stent?
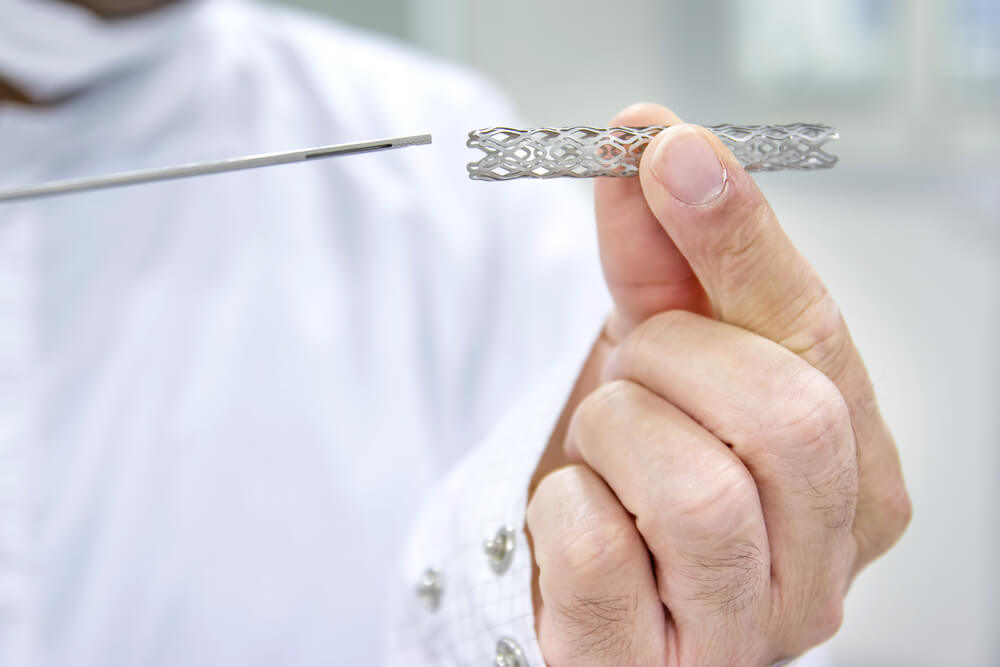
A stent is a small plastic or metal tube in the shape of a net that a specialist places in a blocked blood vessel of the patient using a catheter.
Some stents can also be coated with drugs, if the patient’s condition requires it. Larger stents are stent grafts and can be placed in larger blood vessels. In addition to plastic and metal, some stents can be made of special fabric.
The doctor decides which stent will be implanted in relation to all the information he has about the patient’s condition and his problem. The stent placement procedure is called percutaneous coronary intervention or stent angioplasty.

Why doctors do stenting?
We have explained to you what a stent is, and now we will give you all the neophonic information about the process of its implementation.
Implantation of a stent is an intervention aimed at opening blood vessels in the place where the blockage occurred. Clogging is most often caused by the accumulation of plaque on the walls of blood vessels.
Plaque forms for a number of reasons, but the main ones include diet, smoking and inactivity, i.e. lack of physical activity in humans. In general, the way we live plays a major role in the health of our blood vessels and heart.
When blockage occurs, the consequences are heart attack or stroke, which leave significant marks on the patient’s condition, and death often occurs.
The use of stents is not limited only to coronary arteries, it can also be used:
- to open the bile ducts
- to open the bronchi
- to open the tubes that carry urine from the kidneys to the bladder
- to prevent aneurysm rupture
How to prepare for stent placement?
Preparation before this intervention will depend on many factors, but it is possible to single out some general steps:
- ask your doctor if you need to stop taking any medications and how soon you should stop taking them
- check if you need to take any medicines
- stop smoking
- if you have any chronic or acute illness please mention it
- do not take water or food the night before stent placement
What does stent placement and recovery look like after the intervention?
Stent placement can be done after a heart attack, but it is even better if it is established before the patient is at risk and the stent can prevent the worst outcome.
Stent insertion is an invasive procedure that is performed under local anesthesia, so the patient is awake, but receives intravenous sedatives and relaxation.
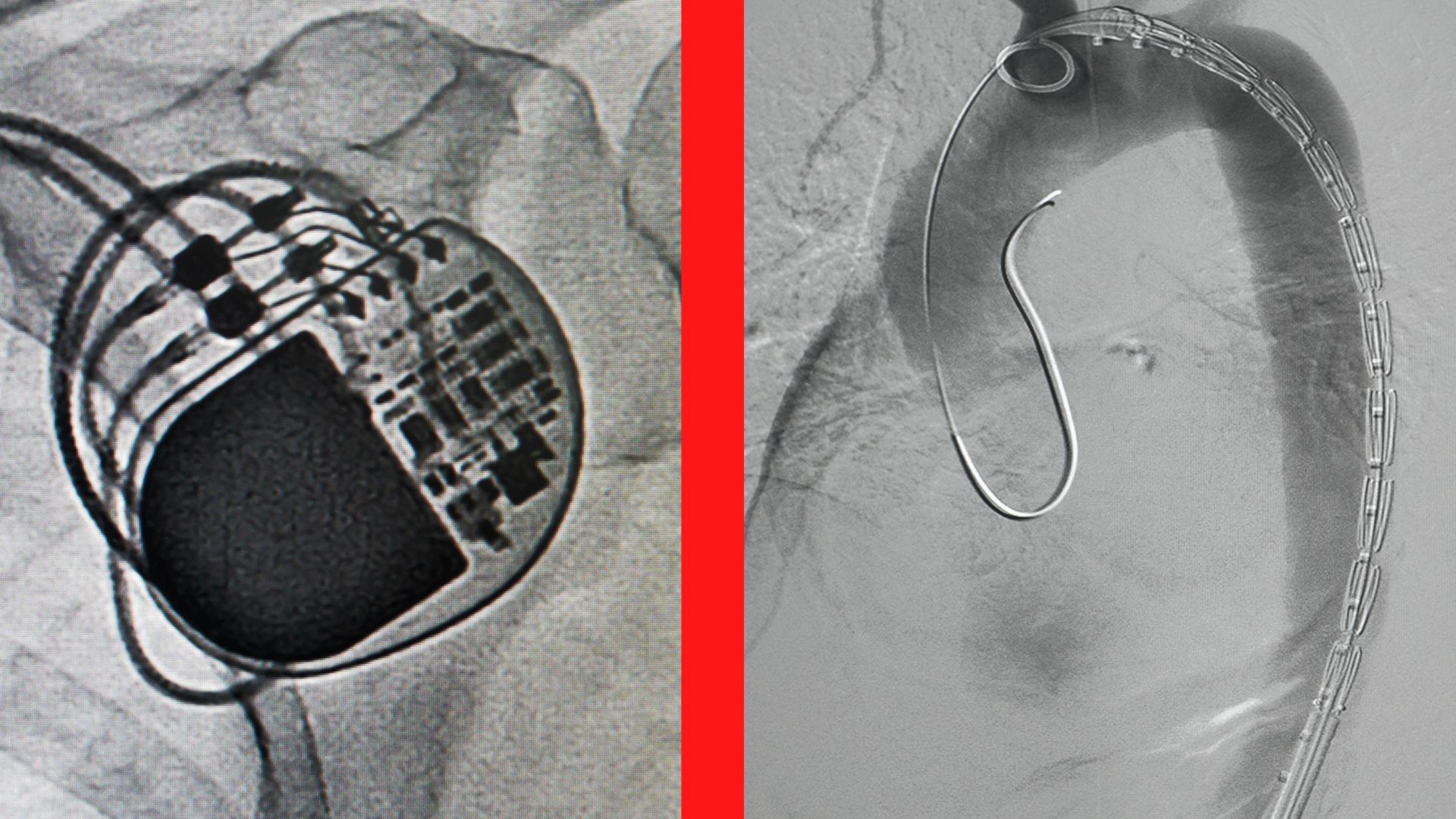
The doctor chooses where to make a small incision through which the catheter will be inserted. Most often, the catheter is introduced through the groin, arm or neck. With the help of the catheter, it is possible to deliver the stent and all the necessary instruments for the intervention to the point of blockage.
When a certain point is reached where the blood vessel is narrowed, the balloon will be inflated, which will enable the expansion of the stent and the stretching of the arteries in order to eliminate the narrowing and enable further uninterrupted blood flow.
When the stent is placed, the catheter is removed, and the stent remains, usually permanently, in the place where it was placed.
Stent implantation is performed in specialized, so-called Cath-labs, and our hospital has one of the best equipped ones in all of Serbia. In one place, there are all the devices and instruments necessary to perform this procedure.
After stenting, recovery is the next goal. After the intervention, the patient will need several days to recover, which is significantly shorter compared to the recovery after the bypass.
It should be emphasized that a stent saves life, but it does not mean that you are completely healthy when you receive it.
Patients then enter into a long-term struggle to preserve their health. The cardiologist prescribes therapy, which must be consistently implemented, but also gives guidelines on how to improve life, and thus protect the heart.
Therapy, a healthy diet, giving up harmful habits, physical activity and regular check-ups should be in the consciousness of every person who has an implanted stent.
Stent implantation risks
Any intervention carries with it risks. In the case of stents, only a specialist can assess whether you are the right candidate for stent implantation and whether complications are possible in your case.
Some of the complications can be:
- allergic reaction to contrast agent or drugs
- breathing problems due to analgesics
- infection
- blocking arteries
- re-narrowing of the blood vessel
- bleeding
- clot formation
- heart attack
- the body rejects the stent
These problems occur rarely, but if you feel afraid of intervention because of them, consult a doctor. Our experts are always at your disposal.
Is physical activity allowed after stent placement?
Physical activity after stent implantation is desirable, but to what extent and intensity it depends on the patient himself, his age, associated diseases, etc.
This intervention is not only carried out in the elderly population, there are more and more severely obese young people for whom a stent can significantly extend their life. It is often difficult for young patients to believe what is happening to them and it is difficult for them to understand that they have to change their habits and behave much more responsibly because somehow we all associate heart disease with older people. Regardless of age, heart disease is dangerous, that must be clear.
The cardiologist should give you instructions immediately, because rehabilitation that includes physical activity should be started as soon as possible.
In any case, a light walk can’t hurt you, and swimming is often recommended for heart patients, where it’s important to take care of the process of entering the water and the length of time you stay in the water, especially if it’s thermal water.
Some patients also benefit from yoga and pilates. The issue of physical activity should be one of your priorities, and you should think carefully about how you will introduce it into your daily routine.
In addition, regular therapy should prevent re-clogging of blood vessels and new complications, progression of the disease and damage to the heart. The doctor will also tell you how often you should do tests and when you should come for check-ups, and you should strictly stick to that schedule, so that in case the situation worsens, you can plan further treatment steps in time.
Heart diseases are extremely dangerous and treatment should not be taken into your own hands. Especially after a heart attack, it is important to follow the cardiologist’s instructions, because prevention of the next one is necessary.
Life with a stent should not be a difficulty and burden for you, you should see it as a new chance, as a new birth and you should organize all your activities and life in such a way that you really take advantage of the opportunity that the stent gave you.
Take care of the activity, give up alcohol and cigarettes, eat healthy, not for the sake of the stent, but for the sake of your heart and new life.
If you are looking for a cardiologist who will be a real ally in your fight for health, make an appointment with us.